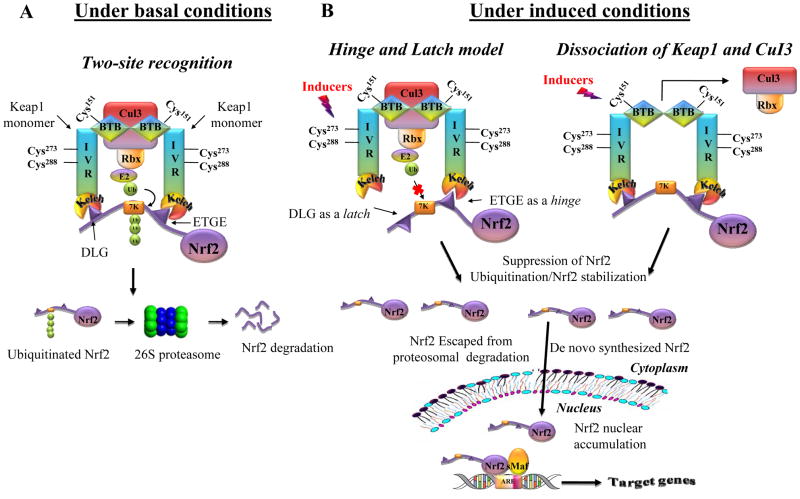
Figure 3.
The proposed regulatory mechanisms of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. (A) Under basal conditions, Nrf2 binds to Keap1 through ETGE (‘hinge’) and DLG (‘latch’) motifs (two-site recognition), and Nrf2 is constantly ubiquitinated by Keap1-Cul3-Ligase complex and degraded in the 26S proteasome (B) Under induced conditions, electrophilic modification of specific Keap1 cysteines induces a conformational change in Keap1 that disrupts the low affinity interaction with DLG (‘latch’) and consequently affects ubiquitination of Nrf2 (‘hinge’ and ‘latch’ model). Alternatively, inducers can cause the dissociation of Keap1-Cul3 complex, which prevents the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of Nrf2.