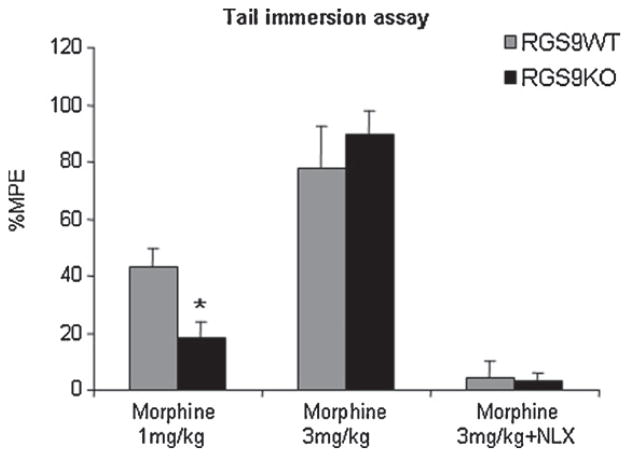
Fig. 2.
RGS9-2 is a positive modulator of morphine analgesia in the tail immersion assay. RGS9KO mice showed decreased sensitivity to morphine in the tail immersion test, at low doses (1 mg/kg s.c.) compared to their RGS9WT controls (n = 11 per genotype). The thermal withdrawal latency is increased in wild-type but not in mutant mice. Both genotypes showed similar analgesic responses (n = 6–8) to morphine at higher doses (3 mg/kg). The analgesic effect of morphine in the tail immersion test is completely blocked following naloxone (NLX) administration (0.3 mg/kg s.c., n = 7–9 per group). Data are expressed as mean MPE ± SEM, *P < 0.05, two way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.