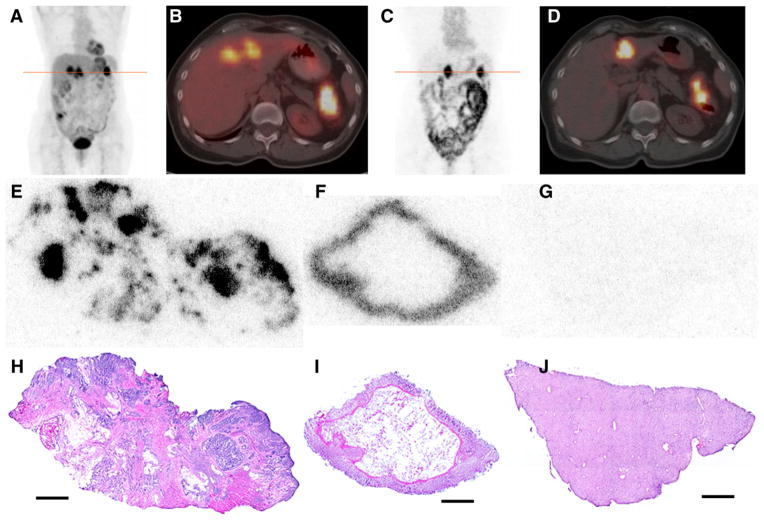
FIGURE 1.
(A–B) 18F-FDG PET/CT scan acquired immediately before administration of 124I-huA33: coronal maximum-intensity-projection image (A) and transaxial PET/CT slice (B) through line of A. Images show pathologic uptake in primary (splenic flexure of colon) and metastatic (liver) lesions together with normal physiologic accumulation. (C–D) Clinical PET/CT scan acquired 162 h after administration of 395 MBq (10.7 mCi) of 124I-huA33: coronal maximum-intensity-projection (C) and transaxial PET/CT slice (D) through line of C. Intense focal uptake is visible in primary and metastatic tumor together with significant uptake throughout normal intestine. (E–J) DAR (E–G) and hematoxylin and eosin–stained (H–J) tissue sections corresponding to features observed in clinical image: primary tumor (E and H), normal colon (F and I), and normal liver (G and J). In tumor section, 124I-huA33 is localized primarily in regions of viable tumor cells with little stromal uptake. Normal colonic mucosa has high and uniform uptake. Little to no uptake is present in normal liver. Scale bars = 2 mm.