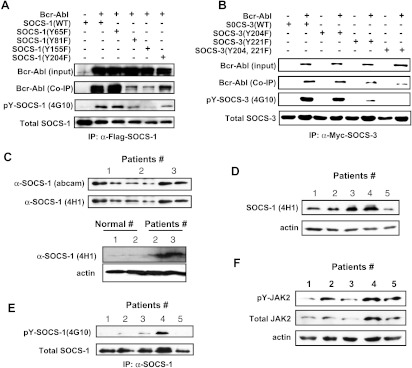
Figure 2.
Identification of Bcr-Abl-dependent phosphorylation sites of SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 and detection of SOCS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in primary CML samples. (A) 293T cells were cotransfected with Bcr-Abl and either SOCS-1 or its mutants as described in Figure 1. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates was performed to examine Bcr-Abl expression. Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag-SOCS-1 antibody, and then precipitated proteins were examined for SOCS-1, Bcr-Abl, and tyrosine-phosphorylated SOCS-1 using antibodies as indicated. (B) Experiments were performed as described in A. 293T cells cotransfected with Bcr-Abl and Myc-tagged wild-type or mutant SOCS-3 were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody (9E10). Shown are immunoblots probed with indicated antibodies. (C) Lysates of peripheral blood white cells from three CML patients were examined using an mAb (4H1) directed against the N-terminal region of SOCS-1 and a rabbit polyclonal Ab directed against C-terminal SOCS box (upper panel). SOCS-1 protein levels were also examined in peripheral blood white cells from normal controls (lower panel). (D) Expression levels of SOCS-1 were examined in five CML samples (patients 1–3 are the same as in C) after normalizing to actin loading control. (E) Lysates derived from the five CML samples in D were immunoprecipitated with anti-SOCS-1 antibody. Precipitated proteins were probed with indicated antibodies by Western blot analysis. (F) Lysates as described in D were used to detect total JAK2 and pJAK2 levels. Shown is an immunoblot probed as indicated.