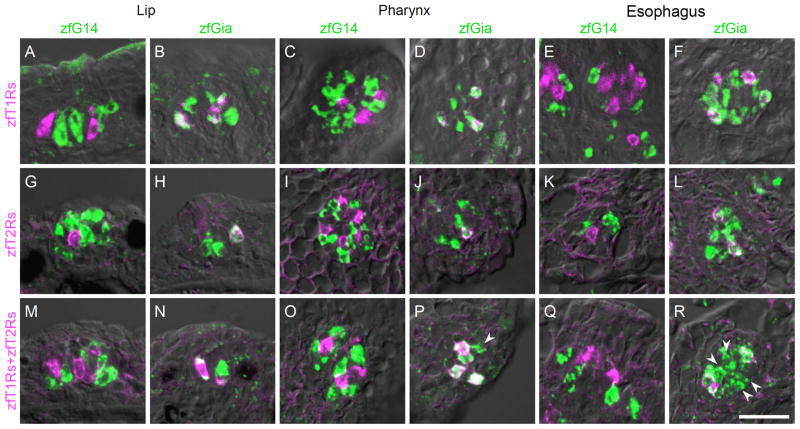
Fig. 6. Molecular characterization of taste receptor cells expressing G14 and Gia in zebrafish gustatory epithelia.
Double-labeled fluorescent in situ hybridization was carried out to examine the relationship between the expression of G alpha subunits and the expression of known taste receptors. The probe for zfT1Rs was a mixture of zfT1R2a, zfT1R2b and zfT1R3 riboprobes, which covers all known T1R-expressing TRCs in zebrafish (Ishimaru et al., 2005). The probe for zfT2Rs was also a mixture of zfT2R1a, zfT2R2a, zfT2R3, zfT2R4, and zfT2R5 riboprobes, which covers all known T2R-expressing TRCs in zebrafish (Ishimaru et al., 2005; Oike et al., 2007; Okada et al., 2010). The probe for zfT1Rs+zfT2Rs was a further mixture of the probes for zfT1Rs and zfT2Rs. G14, Gia, and zfT1Rs (A–F); G14, Gia, and zfT2Rs (G–L); and G14, Gia, and all known zebrafish taste receptors (M–R). Both zfT1Rs and zfT2Rs were co-expressed with zfGia (A–L). White arrowheads indicate zfGia-expressing cells that lack zfT1R and zfT2R expression (P and R). n≥2, number of sections ≥10 for each examination. Scale bar: A–R (in R), 20 μm.