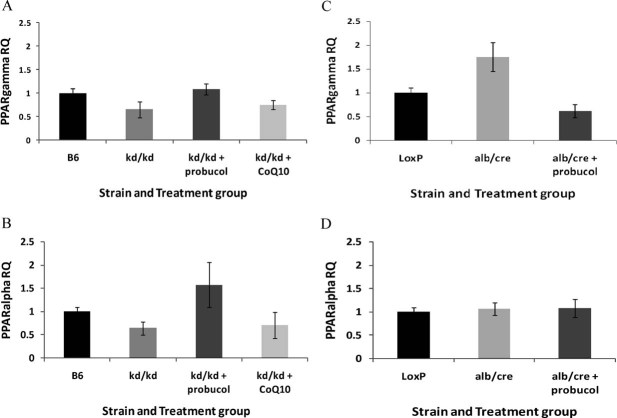
Figure 5. PPAR transcription factor expression normalizes with probucol therapy in Pdss2 mutant mice.
- Hepatic expression of PPAR-γ and
- PPAR-α in Pdss2 missense mice is decreased by quantitative RT-PCR validation, but increased by long-term probucol supplementation either to (PPAR-γ) or exceeding (PPAR-α) expression levels seen in B6 WT controls. CoQ10 supplementation does not significantly alter expression of either PPAR transcription factor in missense mutants. n = 4 female mice per strain and treatment group aged 129–156 days.
- Hepatic expression of PPAR-γ is increased by quantitative RT-PCR validation in liver-conditional Pdss2 knockout mice relative to LoxP WT controls, but clearly decreased by long-term probucol therapy below expression levels seen in WT controls.
- In contrast, hepatic PPAR-α expression is unchanged in male liver-conditional Pdss2 knockout mice either on standard chow or supplemented long-term with probucol relative to LoxP WT controls. n = 3 male mice per strain and treatment group aged 120–141 days.