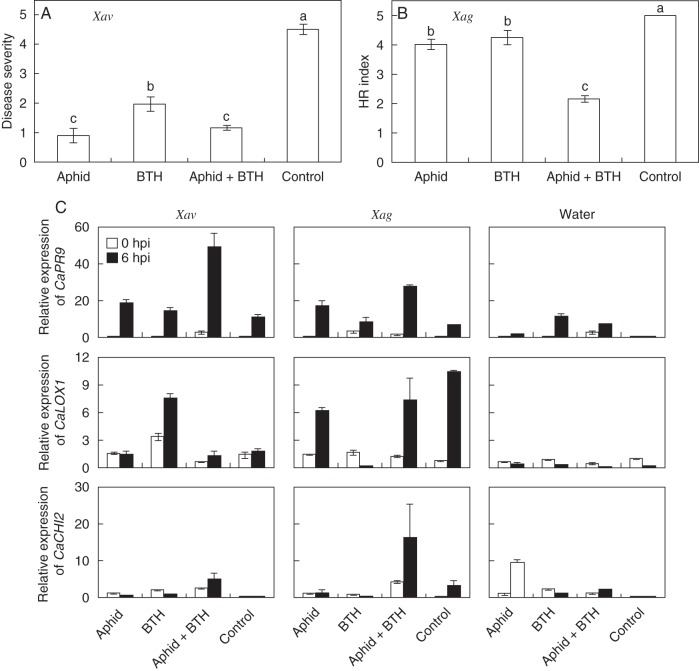
Fig. 1.
Induction of plant defence responses against compatible and incompatible pathovars of Xanthomonas axonopodis and defence priming of resistance genes by aphid infestation. (A) Induction of plant resistance against a compatible X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria (Xav). Disease severity was measured 7 d after Xav challenge, on a scale of 1–5. (B) Induction of plant resistance against an incompatible X. axonopodis pv. glycines (Xag). The hypersensitive response (HR) index was measured 48 h after Xag inoculation, on a scale of 1–5. Values are means ± s.e.m., sample size n = 10 plants per treatment. Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments (P = 0·05), according to the least-significant difference (LSD) test. (C) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of marker genes for SA (CaPR9), JA (CaLOX1) and ET (CaCHI2) in aphid, 0·5 mm BTH, aphid + BTH and water control at 0 and 6 h post-inoculation (hpi). The housekeeping gene CaActin was used as a control. Values are means ± s.e.m. The experiment was repeated four times with similar results.