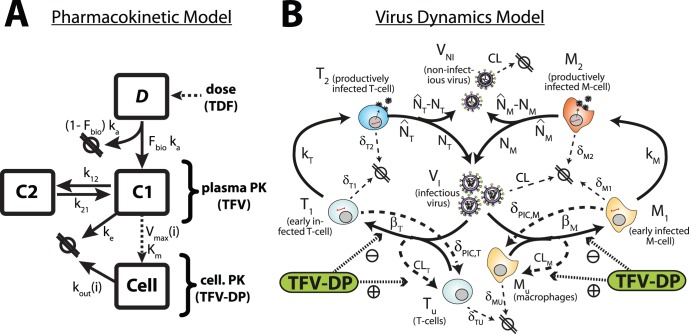
Figure 1. Pharmacokinetic model of TFV and intracellular TFV-DP and model of viral kinetics.
A: Pharmacokinetic model. Parameters 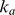 and
and 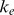 are the absorption and elimination rate constants of the central compartment C1 (which resembles plasma pharmacokinetics of TFV) respectively. The parameters
are the absorption and elimination rate constants of the central compartment C1 (which resembles plasma pharmacokinetics of TFV) respectively. The parameters 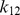 and
and 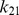 denote the influx and outflux rate constant to-/from the peripheral compartment C2 respectively. Both compartments (central-/peripheral-) have the same volume of distribution
denote the influx and outflux rate constant to-/from the peripheral compartment C2 respectively. Both compartments (central-/peripheral-) have the same volume of distribution 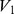 . The dotted line from the central compartment to the intracellular compartment C3 represents subsumed processes, namely the cellular uptake of TFV and subsequent phosphorylation to TFV-DP, which were related to the plasma concentration of TFV (C1) by Michaelis-Menten kinetics, with parameters
. The dotted line from the central compartment to the intracellular compartment C3 represents subsumed processes, namely the cellular uptake of TFV and subsequent phosphorylation to TFV-DP, which were related to the plasma concentration of TFV (C1) by Michaelis-Menten kinetics, with parameters 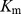 and individual parameter
and individual parameter 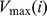 . The parameter
. The parameter 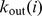 is the individual, cellular elimination rate constant of TFV-DP. B: Virus dynamics model. T-cell and macrophage target cells (
is the individual, cellular elimination rate constant of TFV-DP. B: Virus dynamics model. T-cell and macrophage target cells (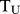 ,
, 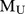 ) can become successfully infected by infective virus
) can become successfully infected by infective virus 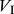 with lumped infection rate constants
with lumped infection rate constants 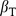 and
and 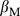 , respectively, creating early infected cells
, respectively, creating early infected cells 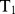 and
and 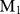 . Infection can also be unsuccessful after the irreversible step of fusion (rate constant
. Infection can also be unsuccessful after the irreversible step of fusion (rate constant 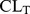 and
and 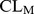 , dashed lines), eliminating the virus and rendering the cell uninfected. Early infected cells
, dashed lines), eliminating the virus and rendering the cell uninfected. Early infected cells 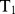 and
and 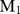 can destroy essential viral proteins or DNA prior to integration with rate constants
can destroy essential viral proteins or DNA prior to integration with rate constants 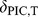 and
and 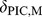 (dashed lines) returning the cell to an uninfected stage. The genomic viral DNA can become integrated with rate constants
(dashed lines) returning the cell to an uninfected stage. The genomic viral DNA can become integrated with rate constants 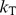 and
and 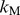 creating late infected cells
creating late infected cells 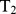 and
and 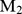 , which can release new infectious- and non infectious virus
, which can release new infectious- and non infectious virus 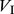 and
and 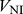 with rate constants
with rate constants 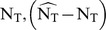 and
and 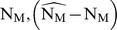 , respectively. All cellular compartments
, respectively. All cellular compartments  can get destroyed by the immune system with respective rate constants
can get destroyed by the immune system with respective rate constants 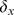 and the free virus gets cleared with rate constant
and the free virus gets cleared with rate constant 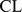 (thin dashed lines). The pharmacologically active form of tenofovir (tenofovir-diphosphate, TFV-DP, green box) inhibits successful cell-infection (parameter
(thin dashed lines). The pharmacologically active form of tenofovir (tenofovir-diphosphate, TFV-DP, green box) inhibits successful cell-infection (parameter 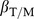 ) and increases the rate of unsuccessful infection (parameter
) and increases the rate of unsuccessful infection (parameter 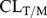 ).
).