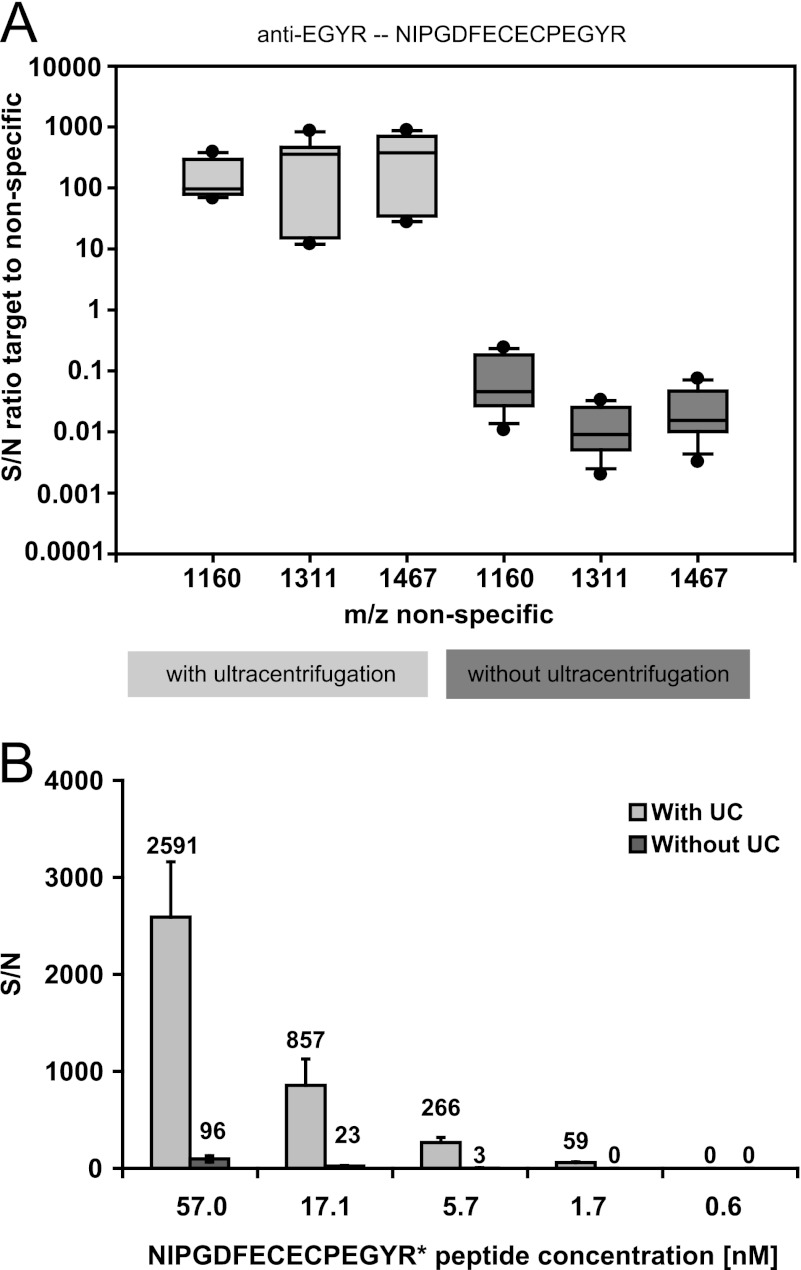
Fig. 4.
Impact of ultracentrifugation step on peptide quantification. A, distribution of signal to noise ratios for target peptide NIPGDFECECPEGYR (m/z 1842.68, vitamin K-dependent protein S) relative to three nonantibody targeted peptides from two different proteins α1-acid glycoprotein 1 (m/z 1160.70, WFYIASAFR) and two peptides from human serum albumin (m/z 1311.77, HPDYSVVLLLR; and m/z 1467.85, RHPDYSVVLLLR) comparing the assay with and without the ultracentrifugation step. The data from three assay replicates are included in one box plot. The signal to noise (S/N) ratios of the values generated with the ultracentrifugation procedure are significantly higher compared with the respective values of the assays without ultracentrifugation (p < 0.001). B, MALDI signal to noise values for different spike-in concentrations of isotopically labeled NIPGDFECECPEGYR* peptide (m/z 1852.73) in TXP assays with plasma digest including and excluding ultracentrifugation. The concentrations refer to 100 μl of reconstituted plasma digest, which are derived from 16 μl of plasma. A representative experiment is shown. The error bars represent the standard deviation of four different MALDI spots of the same sample.