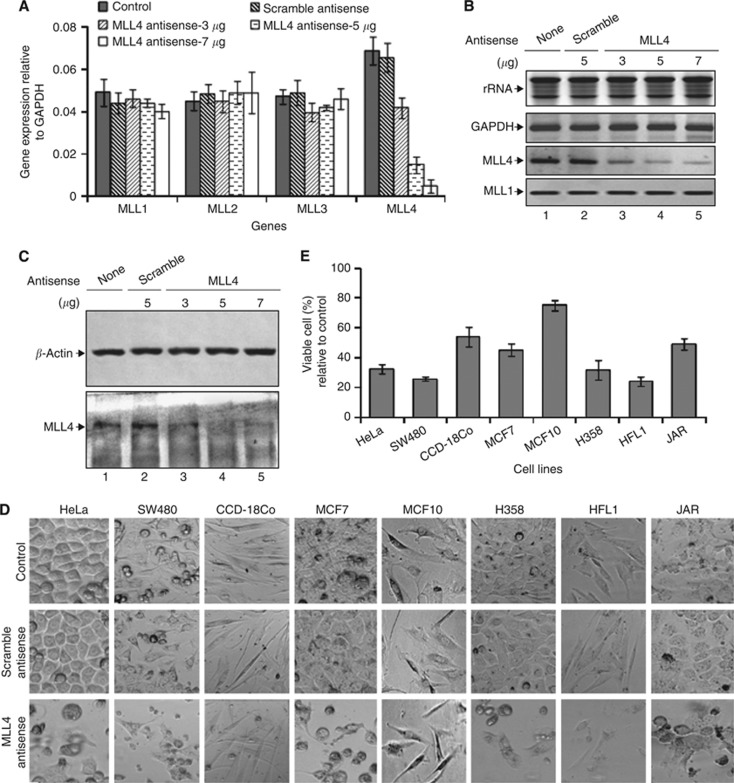
Figure 1.
MLL4 knockdown and its effect on cell viability. (A) Effect of MLL4 knockdown on the expression of MLL1–4: colon cancer (SW480) cells were transfected with varying concentrations of MLL4 antisense for 48 h. RNA was reverse transcribed and subjected to real-time PCR analysis using primers specific to MLL1, MLL2, MLL3, MLL4 and GAPDH. The expression of different MLLs relative to GAPDH was plotted. GAPDH expression and rRNA levels were used as loading control. Each experiment was performed in three replicates for at least two times. Bars indicate standard errors. (B) RNA from the control and MLL4 antisense-treated cells were subjected to RT–PCR using primer specific to MLL4, MLL1 (specificity control) and GAPDH (loading control) and then analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1: control cells; lane 2: cells transfected with scramble antisense; lanes 3–5: cell transfected with 3–7 μg of MLL4 antisense. (C) Western blotting: proteins from the control and MLL4 antisense-treated cells were subjected to western blotting using anti-MLL4 and anti-β-actin antibodies (loading control). (D) Microscopic images showing different cancer and non-cancer cells transfected with MLL4 or scramble antisense for 48 h. Control cells were treated with PBS (buffer) alone. (E) MTT assay: cells were transfected with 7 μg MLL4 or scramble antisense for 48 h and then subjected to MTT assay. The relative (%) cell viability (MLL4 antisense vs scramble antisense) was plotted for different cell lines. Bars indicate standard errors.