Figure 1.
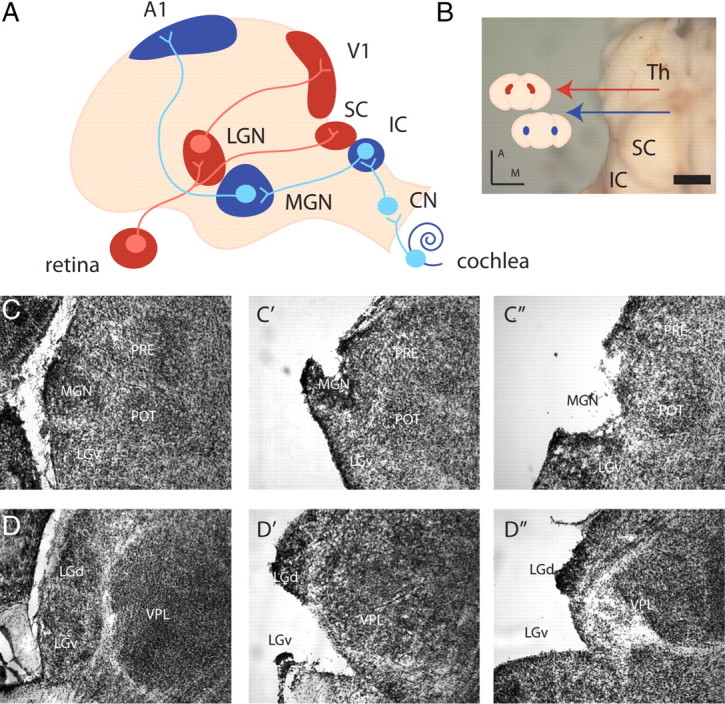
Primary visual and auditory sensory pathways to the cortex. A, Retinal ganglion cells project to the LGN, which in turn projects to V1. Auditory afferents from the cochlea terminate in the cochlear nucleus (CN) of the brainstem, which then innervates the IC. Cells from the IC project to the MGN, which in turn projects to A1. B, Dorsal view of the neonatal thalamus (the cortex has been peeled off), red arrow, LGN; blue arrow, MGN; Th, thalamus. Scale bar, 1 mm. Colored lines show coronal planes of section for Nissl stains and point to schematics of coronal sections featuring the MGN (blue) and LGN (red). C, D, Coronal sections of cresyl violet stains reveal the nuclear structure of the MGN (C) and LGN (D) at P0. Two examples of MGN (C′, C″) and LGN (D′, D″) dissected brain are representative of the tissue samples taken for microarray analysis. PRE, Pretectal nucleus; POT, posterior thalamic nucleus; VPL, ventral posterior thalamic nucleus, lateral part; LGv, ventral subdivision of the LGN; D, dorsal; M, medial. Scale bar, 150 μm.
