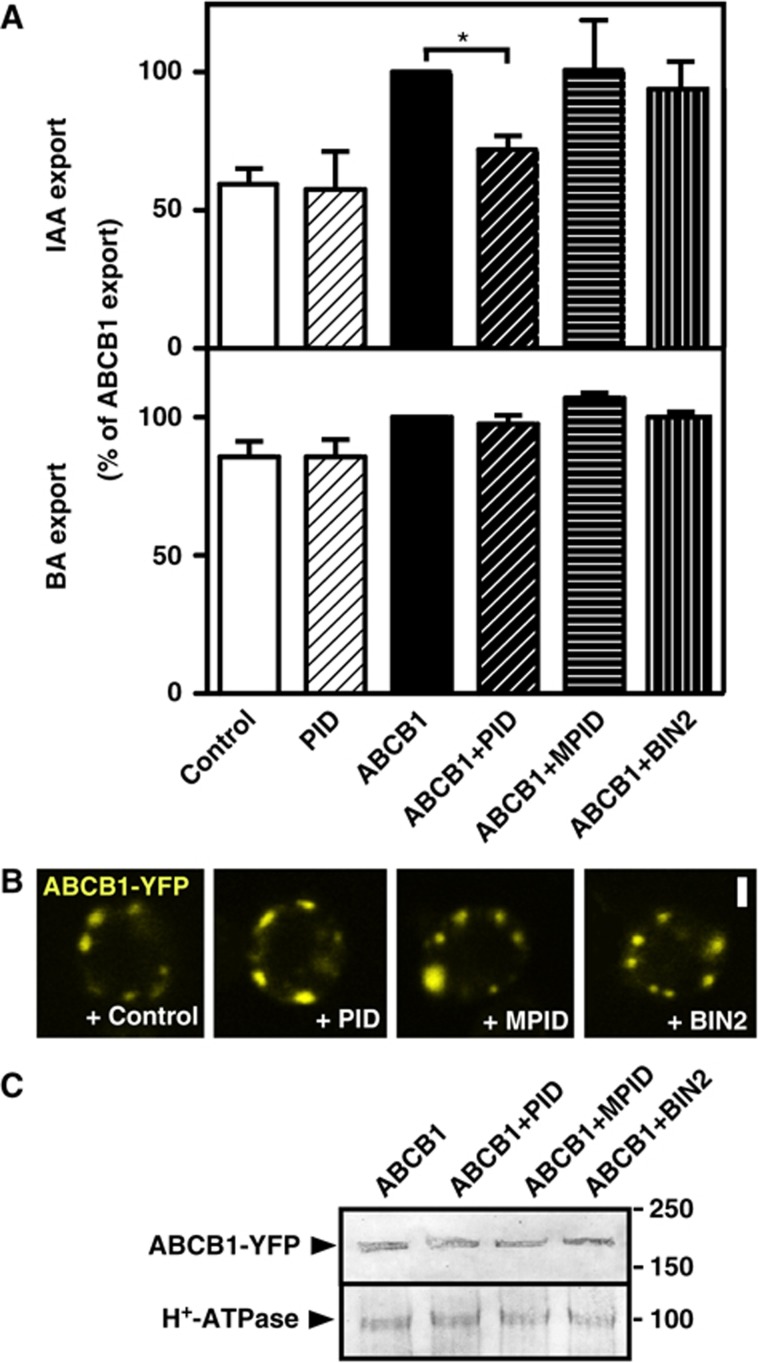
Figure 2.
PID modulates ABCB1-mediated auxin efflux in yeast. (A) PID specifically inhibits ABCB1-mediated IAA export, while a mutated, inactive PID, MPID or unrelated protein kinase, BIN2, has no significant effect. Reduction of auxin retention (export) was calculated as relative export of initial export where ABCB1 was set to 100% (mean±s.e.; n=4–10). Significant differences (unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, P<0.05) between –PID controls are indicated by asterisks. (B, C) Co-expression with PID, MPID or BIN2 does not significantly alter location (B) and expression (C) of ABCB1-YFP as revealed by confocal microscopy (B) and western analysis (C). Each 20 μg of protein was subjected to PAGE and western analysis using anti-GFP and plasma-membrane marker, anti-PMA1 (H+-ATPase). ABCB1-YFP localizes primarily to raft-like structures and the plasma membrane (see Supplementary Figure S2; Bailly et al, 2008). Bar, 2 μm.