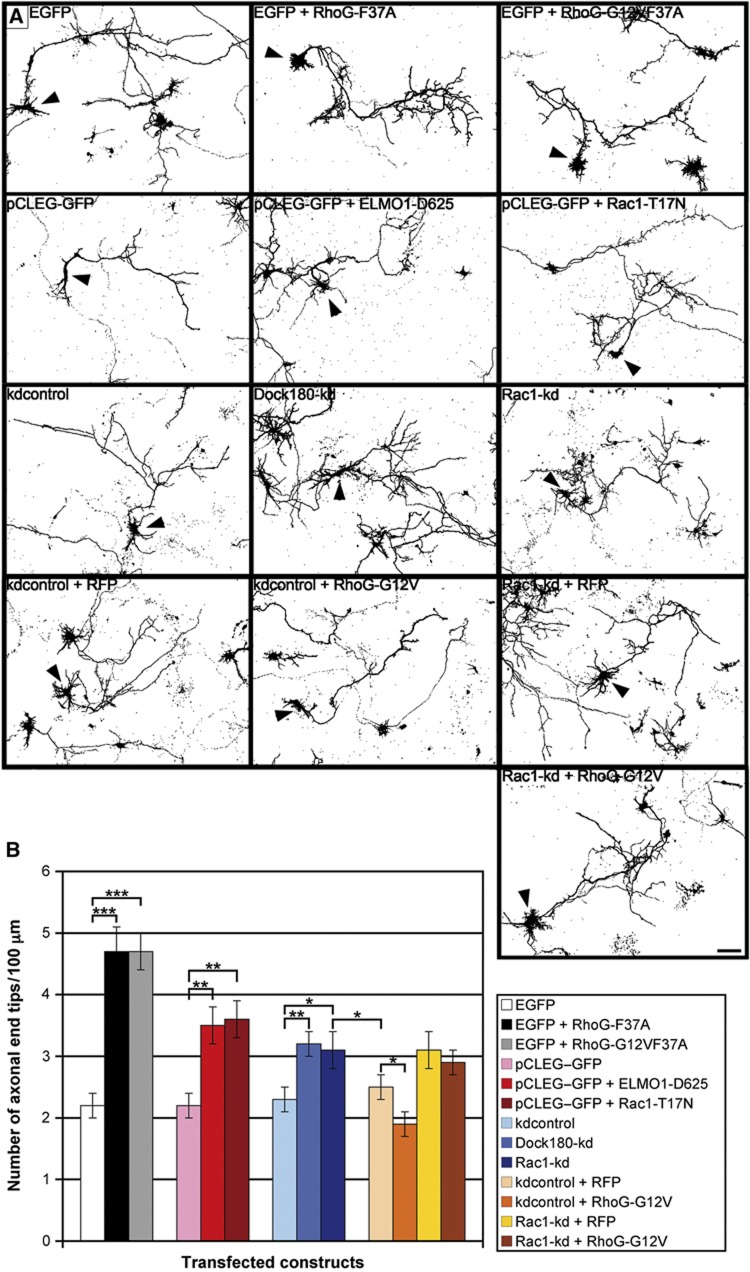
Figure 3.
RhoG inhibits axonal branching via ELMO/Dock180/Rac1 signalling. (A) The axonal morphology of hippocampal neurons, transfected with the indicated constructs at DIV2, was analysed after staining for GFP at DIV2+2 (arrowheads). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) RhoG-F37A and RhoG-G12VF37A, RhoG mutants that cannot bind to ELMO, strongly increased the number of axonal end tips. The same effect was determined for ELMO-D625, Rac1-T17N, Dock180-kd, and Rac1-kd. Under the condition of Rac1 knockdown, RhoG-G12V did not decrease the number of axonal end tips. Mean values (n=80 neurons for Dock180-kd and kdcontrol, n=40 neurons for all other conditions)±s.e.m. (***P<0.0005; **P<0.005; *P<0.05).