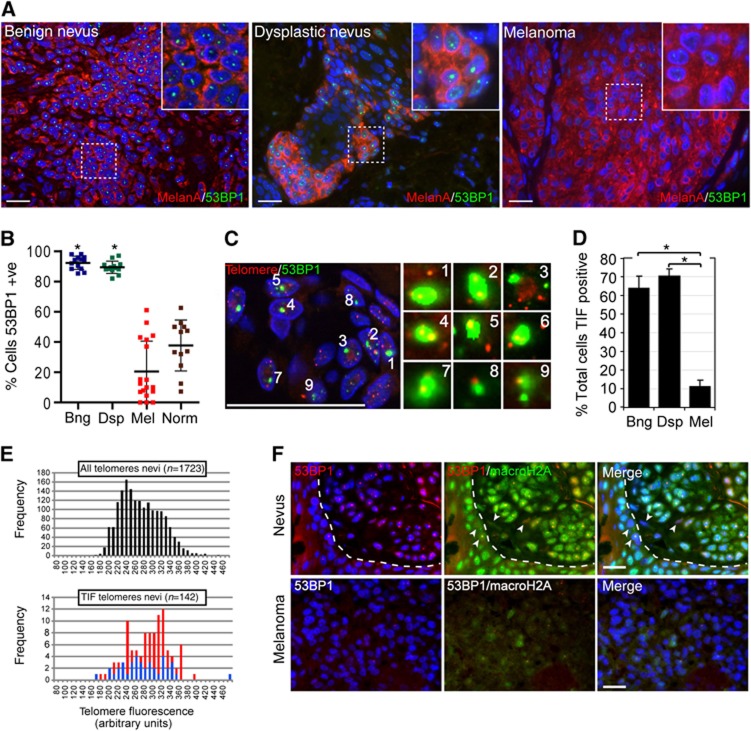
Figure 1.
Melanocytic cells of benign- and dysplastic nevi, but not cells of malignant melanoma, display hallmarks of telomere dysfunction-induced cellular senescence. (A) Tissue sections from indicated lesions were immunostained with antibodies against melanA (red) and 53BP1 (green). Insets display an enlarged section of the indicated area. (B) Quantitation of 53BP1-positive melanocytic cells in benign nevi (Bng; n=13, 3529 cells), dysplastic nevi (Dsp; n=13, 2300 cells), melanoma (Mel; n=18, 5401 cells), and in normal epidermal melanocytes adjacent to the lesion (Norm; n=12, 485 cells). Values are shown as mean±s.d.; *P<0.001. (C) Dysfunctional telomeres in nevi. Tissue sections from benign nevi were processed by immunoFISH to simultaneously detect 53BP1 (green) and telomeres (red). Enlarged versions of the numbered DNA damage foci showing colocalization with telomeres are shown in the right micrographs. Note that only one optical slice is displayed. (D) Quantitation of TIF positive cells in indicated lesions (mean±s.d.). A total of 13 benign nevi (1355 53BP1 foci), 13 dysplastic nevi (2968 53BP1 foci), and 7 melanoma (891 53BP1 foci) were counted; *P<0.001. (E) Distribution of telomere lengths based on their signal intensities (x-axis; arbitrary units). Top histogram: all telomeric signals in cells of nevi (average signal intensity 268±46). Bottom histogram: single (red bars; average signal intensity 281±46) and multiple/diffuse (blue bars; average signal intensity 275±56) telomeric signals associated with 53BP1 foci. n: number of telomeric signals analysed (F) Tissue sections from a dysplastic naevus (top), and invasive melanoma (bottom) were immunostained using antibodies against 53PB1 (red) and macroH2A (green). Arrows point to stromal cells and basal layer epidermal keratinocytes that did not display elevated macroH2A levels. Dashed line separates epidermis (bottom left) from naevus (top right). Scale bars: 25 μm. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.