Figure 1. A general overview of cochlear injury and targets or approaches in prevention.
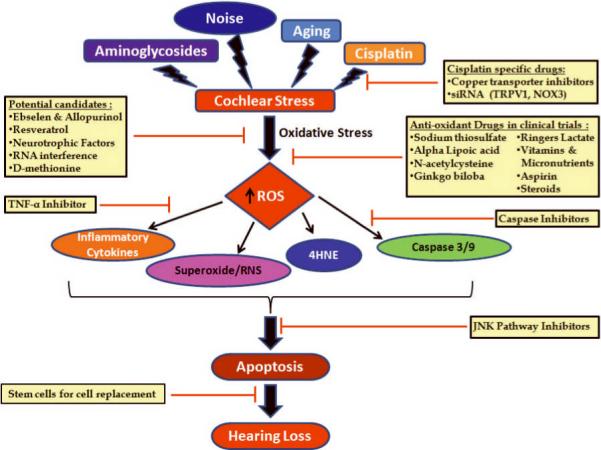
Acquired sensorineural hearing loss has been chiefly subdivided into 4 main categories hearing loss due to aminoglycosides, aging, noise exposure and cisplatin treatment. While each of these ototoxic agents and aging have their own specific molecular pathways causing hearing loss, they all produce oxidative stress, leading to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Most of the drugs in clinical trials as well as the potential candidate drugs target increased ROS generation. Some of the latest drugs or approaches in prevention of sensorineural hearing loss target the downstream effector molecules like TNF-α, caspases, stress pathways and partial or complete replacement of dead and damaged sensory hair cells.
