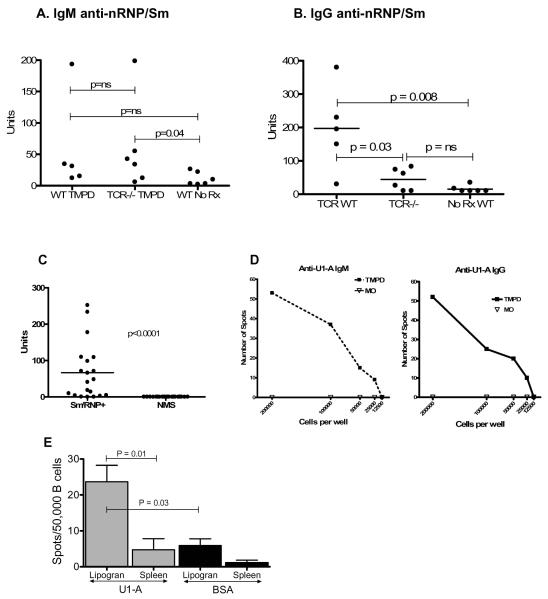
Figure 6. IgG anti-nRNP/Sm autoantibody production in TMPD-treated mice is T cell dependent.
A and B, Serum samples were obtained from wild type C57BL/6J (WT, n = 5) or B6.129P2-Tcrbtm1MomTcrdTm1Mom (n = 6) mice treated 3 months earlier with TMPD. IgM (A) and IgG (B) anti-nRNP/Sm antibody levels were measured by ELISA at a 1:500 serum dilution. Means were compared by the Mann-Whitney test. C, Reactivity of sera with recombinant U1-A protein (ELISA). Recombinant 6His-tagged U1-A protein was expressed in E. coli and purified on a Ni-NTA affinity column. Sera from 20 TMPD-treated BALB/c mice positive for anti-Sm/RNP autoantibodies and 20 normal BALB/c mouse sera were tested for reactivity with the recombinant antigen at a 1:100 dilution (ELISA). D, IgM and IgG ELISPOT assay with purified U1-A antigen using cells isolated from collagenase treated ectopic lymphoid tissue from an anti-RNP positive TMPD-treated mouse or an anti-RNP negative mouse treated with medicinal mineral oil. Representative of 3 experiments. E, IgG ELISPOT assay with purified U1-A or bovine serum albumin (BSA) antigens, using cells isolated from lipogranulomas (Lipogran) or spleens of anti-U1-A positive mice (n = 5). The frequencies of antigen-specific spots are expressed per 50,000 B cells. The frequency of anti-U1-A spots was higher in lipogranulomas than in spleen (P = 0.01, Mann-Whitney test) and the frequency of anti-U1-A spots was higher than the frequency of anti-BSA spots (P = 0.03, Mann-Whitney test).