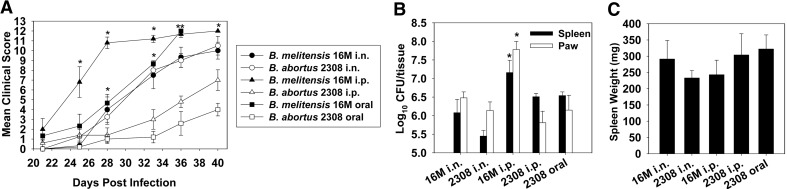
Figure 3. B. melitensis and B. abortus induce joint inflammation in IFN-γ−/− mice independent of route of infection.
IFN-γ−/− mice (BALB/c background, five to seven/group) were infected i.n. (2×104 CFUs), i.p. (2×104 CFUs), or orally (2×1010 CFUs) with B. melitensis 16M or B. abortus 2308. (A) Disease severity was monitored over time, as described, and colonization of the (B) spleens and paws and (C) splenic weights was determined on Day 40 postinfection (mice infected orally with B. melitensis became moribund and were euthanized on Day 36). Error bars represent sem; *P < 0.05, as compared with mice infected with B. abortus via the same route; at this time point, mean clinical scores in mice infected both orally and i.p. with B. melitensis were significantly greater (P < 0.05), than mice infected with B. abortus via the same route.