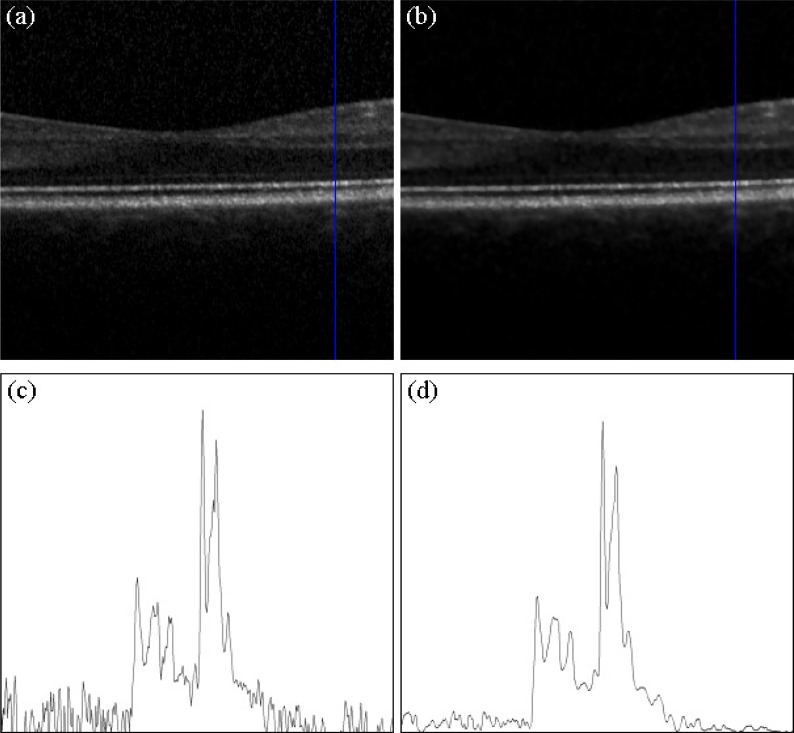
Fig. 2.
(a) Input B-scan recorded with the Spectralis OCT centered on a healthy human macula. (b) Processed speckle noise suppression with the Bayesian estimation approach. (c) Sampled A-scan of the raw image. The noise component is strong and blurs the original signal. (d) Sampled A-scan of the suppressed image. The noise component is much lower and the retinal structures are preserved.