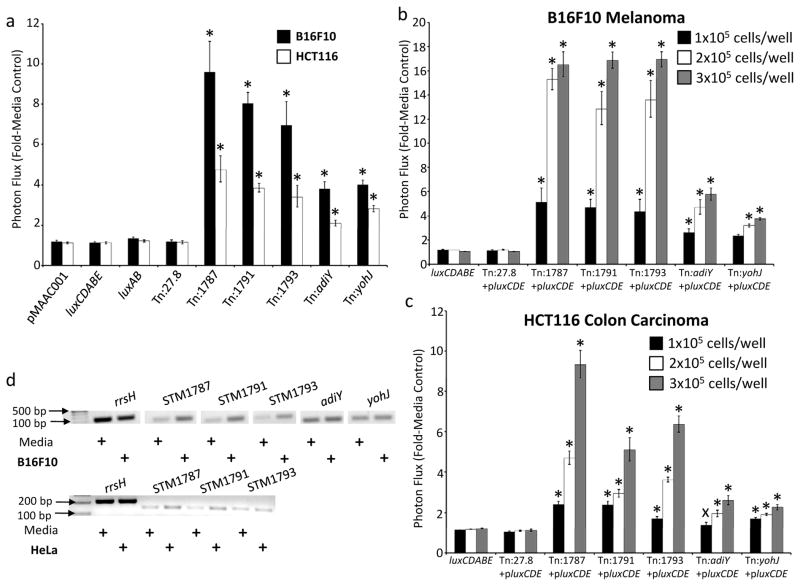
Figure 2. Verification of Salmonella gene activation events in the context of tumor cell co-culture.
(a) Salmonella reporter clones displaying gene activation signals during co-culture with tumor cell lines (black bars, B16F10 cells; open bars, HCT116 cells). Salmonella strains luxAB and Tn:27.8 contain chromosomal luxAB genes under constitutive promoter control; luxCDABE Salmonella contain the full luciferase operon inserted into the chromosome; pMAAC001 constitutively expresses plasmid-encoded luxCDABE. (b, c) Salmonella reporter clones display dose-responsive gene activation in co-culture with B16F10 and HCT116 cells. Bacteria were co-cultured with 1×105, 2×105, or 3×105 B16F10 or HCT116 cells/well. Data were normalized as the ratio of the signal in the condition of interest to signal in media alone. Error bars correspond to SEM. All p value calculations are between luxCDABE and the group indicated by the symbol: * p ≤ 1×10−7; xp ≤ 0.06. (d) Semi-quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR with wild-type SB300A1 bacteria verifies that genes identified by the reporter transposon screen in Salmonella are activated during co-culture with B16F10 melanoma and HeLa tumor cells. rrsH = ribosomal RNA.