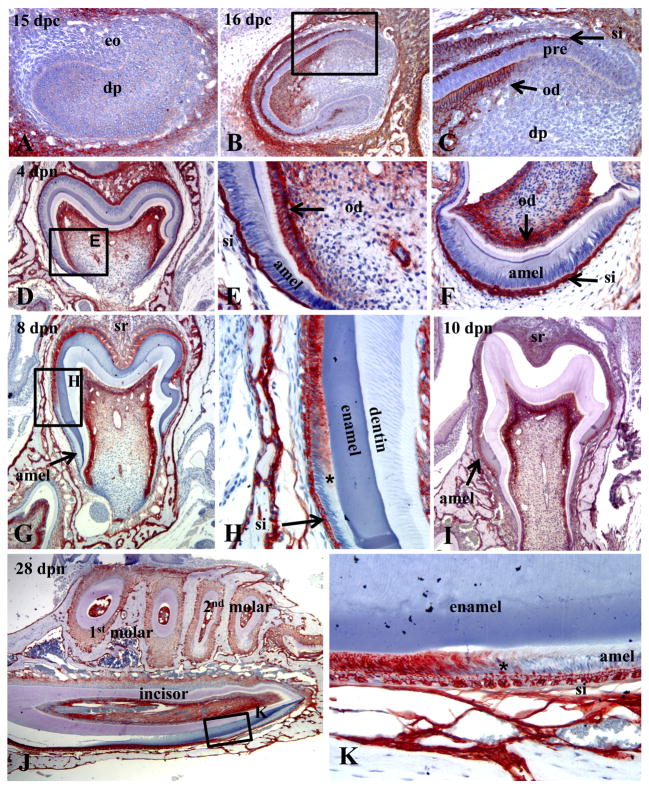
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemistry showing the spatiotemporal expression of TNAP in the healthy (WT) developing enamel organ of fetal and postnatal mice. (A) No TNAP expression is observed in the late cap/early bell stage of the E15 mandibular first molar, before the appearance of the enamel and dentin matrices. (B, C) At E16, the developing maxillary incisor shows TNAP expression in odontoblasts as well as the stratum intermedium (SI) of the enamel organ. Pre-ameloblasts were not observed to be positive for TNAP. (D, E) Localization of TNAP to odontoblasts, as well as SI and stellate reticulum at the 4 dpn mandibular first molar bell stage. (F) Coronal sections of the mandibular incisor at 4 dpn confirms TNAP expression in the SI, but not in ameloblasts during the bell stage. (G, H) By 8 dpn, induction of TNAP expression was localized to ameloblasts of the first mandibular molar, in association with transition (*) from secretory-stage to maturation-stage. ameloblasts (I) By 10 dpn, when the entire ameloblast layer of the first mandibular molar had transitioned to maturation stage, the entire layer was found to be TNAP positive. (J, K) Sagittal sections of the mandibular incisor at 26 dpn confirmed induction of TNAP in ameloblasts at transition (*) from the secretory to maturation stage, while the SI is TNAP-positive over the entire course of incisor amelogenesis and eruption. eo = enamel organ; dp = dental papilla; pre = pre-ameloblasts; SI = stratum intermedium; od = odontoblasts; amel = ameloblasts; SR = stellate reticulum.