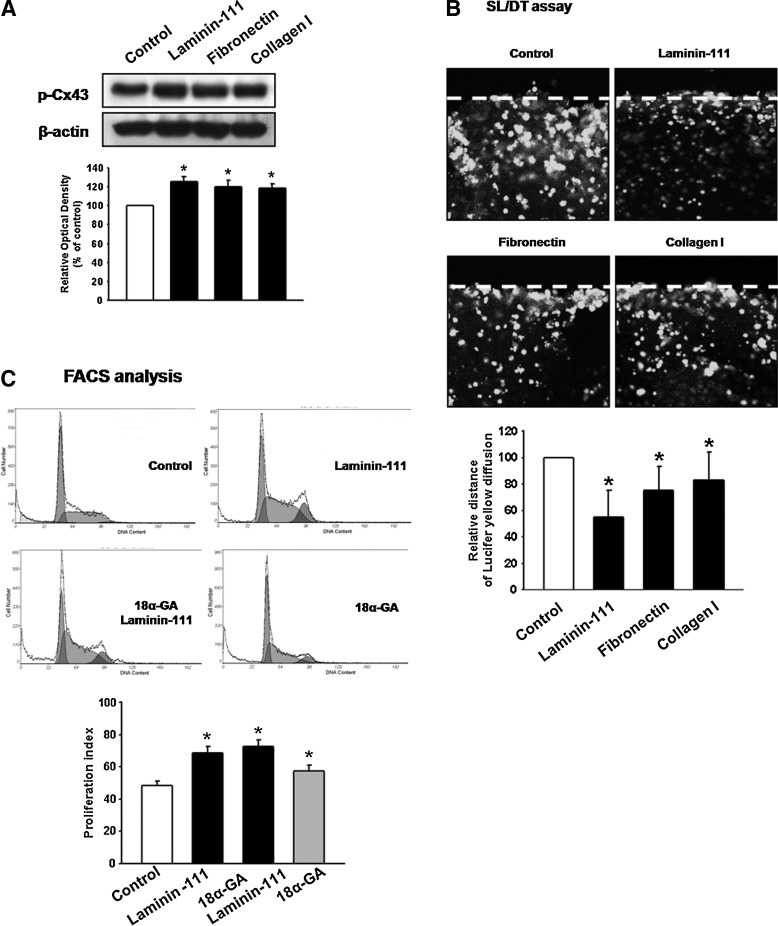
FIG. 1.
Effect of extracellular matrix (ECM) component functional change on Cx43 and related mouse embryonic stem cell (mESC) proliferation (A) Cells were treated with laminin-111, fibronectin, or collagen I (10 μg/mL) for 30 min and the expression of p-Cx43 detected by western blot. The lower panel depicts the mean±standard deviation (SD) of four independent experiments for each condition as determined from densitometry relative to β-actin. *P<0.05 versus control. (B) Cells were treated with laminin-111, fibronectin, or collagen I for 30 min, and gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) analysis was carried out using a scrape loading/dye transfer (SL/DT) assay, as described in the Materials and Methods section. The lower panel depicts the mean±SD of five independent experiments for each condition as determined from quantification of GJIC (the relative distance of Lucifer yellow diffusion compared with control). *P<0.05 versus control. (C) Cells were treated with 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA, gap junction disruptor; 10 μg/mL) for 30 min before laminin-111 treatment for 24 h, harvested, and subjected to propidium iodide (PI) staining for cell-cycle analysis by flow cytometry. Gates were configured manually to determine the percentage of cells in S phase based on DNA content. Data are calculated using proliferation indices [(S+G2/M)/(G0/G1+S+G2/M)]×100 and reported as mean±SD of four independent experiments, each conducted in triplicate. *P<0.05 versus control.