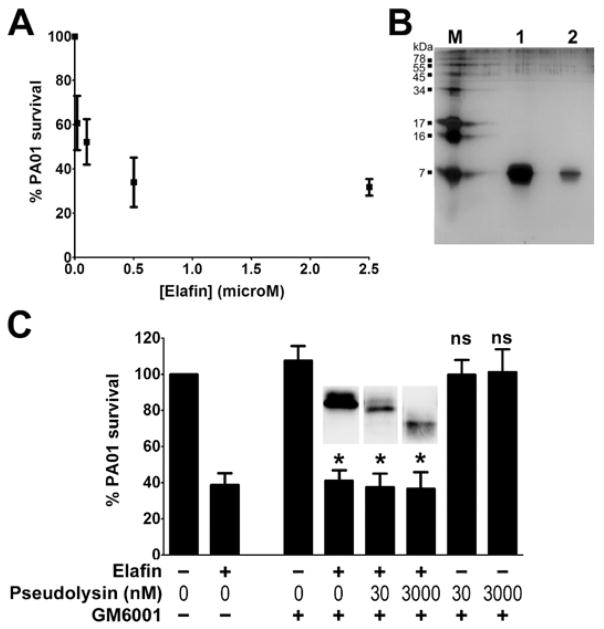
Figure 8. Effect of purified pseudolysin on the antibacterial activity of recombinant elafin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.
(A) Dose-response effect of elafin on P. aeruginosa PAO1 survival. Various concentrations of elafin (0 to 2.5 μM) were incubated with P. aeruginosa PAO1 for 2h. Colonies were counted and the results were expressed as percentage of bacteria survival. Values are means ±SEM (n=5). (B) Purity of recombinant elafin assessed by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. M: Molecular marker; lane 1: 1 μg elafin; lane 2: 200 ng elafin. (C) Effect of pseudolysin-cleaved elafin on P. aeruginosa PAO1 survival. Recombinant elafin (0 or 41.6 μM) was treated with increasing concentrations of pseudolysin (0, 30 and 3000 nM) for 2h and treated with or without GM6001 as indicated in the figure. Samples (diluted 41.6 times) were incubated with P. aeruginosa PAO1 for 2h. Bacterial survival was determined by counting the colony-forming units. Results are expressed as percentage of PAO1 survival. Values are means ±SEM (n=5). One-way ANOVA was performed to determine the statistical significance of the effects of elafin and concentrations of pseudolysin on PAO1 survival (* P<0.05; ns, non significant). Insets represent elafin integrity determined by Western blot under non-reducing conditions.