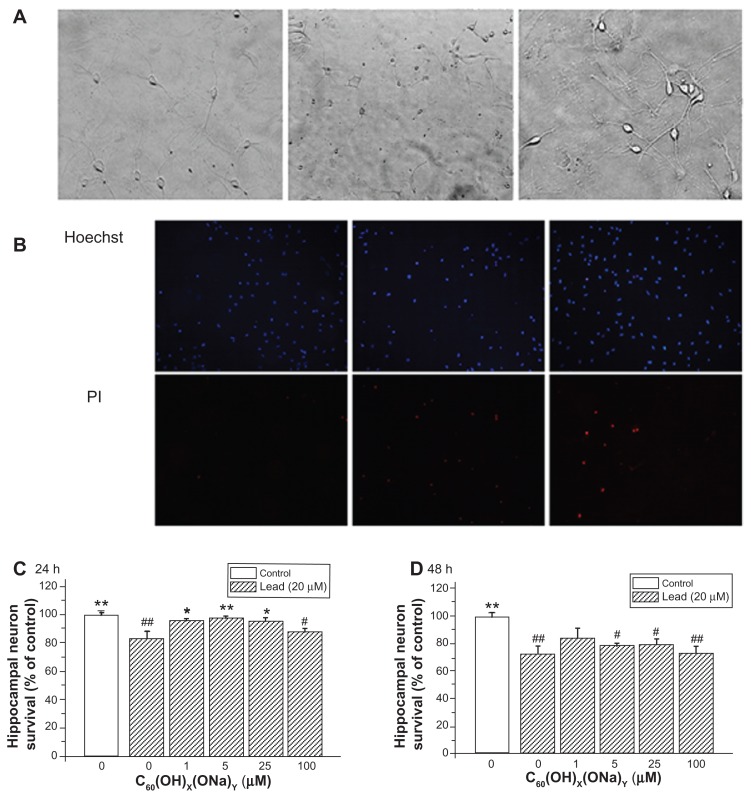
Figure 4.
Protective effect of C60(OH)x(ONa)y against lead-induced neurotoxicity. Hippocampal neurons were treated with various concentrations of fullerenol 0, 1, 5, 25, and 100 μM and lead 20 μM for 24 or 48 hours. The Hoechst dye entered into normal cells and emitted blue fluorescence, while the propidium iodide dye entered into necrotic cells and emitted red fluorescence. (A) Three typical images of random fields per treatment group detected with a high-power optical microscope. Left, control; middle, 20 μM lead-exposed for 24 hours; right, 20 μM lead and 1 μM fullerenol exposed for 24 hours. Magnification is 10 × 20. (B) Three typical images detected with fluorescence microscopy. (C) Survival rate of hippocampal neurons after coculturing for 24 hours. (D) Survival rate after coculturing for 48 hours.
Notes: *P < 0.05 versus lead-exposed group without fullerenol. **P < 0.01 versus lead-exposed group without fullerenol. #P < 0.05 versus control group; ##P < 0.01 versus control group. One-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post hoc tests.