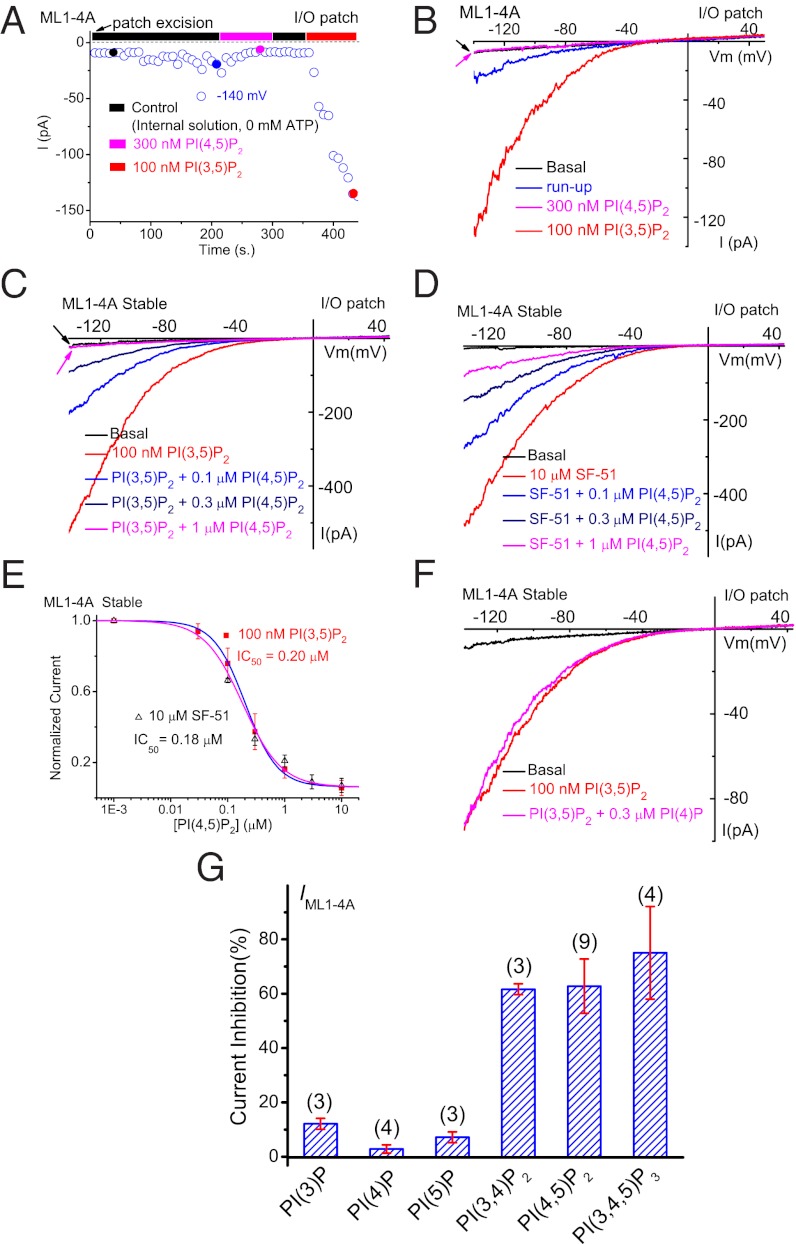
Fig. 2.
Agonist-induced TRPML1 channel activity at the PM is suppressed by PI(4,5)P2. (A) IML1-4A gradually underwent run-up in an I/O patch, and were inhibited by PI(4,5)P2 and activated by PI(3,5)P2. IML1-4A were recorded from I/O patches with repeated voltage ramps (from –140 to +140 mV; 400 ms; 4-s interval between ramps). Only a portion of the voltage is shown. Current amplitudes measured at –140 mV were used to plot the time dependence of the PIP2 effects. The post–run-up IML1-4A was strongly inhibited by 300 nM PI(4,5)P2 but robustly reactivated by 100 nM PI(3,5)P2. (B) Representative traces of IML1-4A at the basal level (pre–run-up), post–run-up, and in the presence of PI(4,5)P2 or PI(3,5)P2, as indicated by colored circles in A. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of PI(3,5)P2-activated IML1-4A by PI(4,5)P2 in an I/O patch from ML1-4A-expressing HEK293 stable cell lines. (D) Dose-dependent inhibition of SF-51–activated IML1-4A by PI(4,5)P2. (E) PI(4,5)P2 inhibited both PI(3,5)P2-activated and SF-51-activated IML1-4A (IC50 = 0.2 μM and 0.18 μM, respectively). (F) PI(3,5)P2-activated IML1-4A was insensitive to PI(4)P (300 nM). (G) Effects of various phosphoinositides on PI(3,5)P2-activated IML1-4A. In all experiments, phosphoinositides (300 nM) were coapplied with PI(3,5)P2 (100 nM). Data are presented as mean ± SEM; numbers (n) are noted in parentheses.