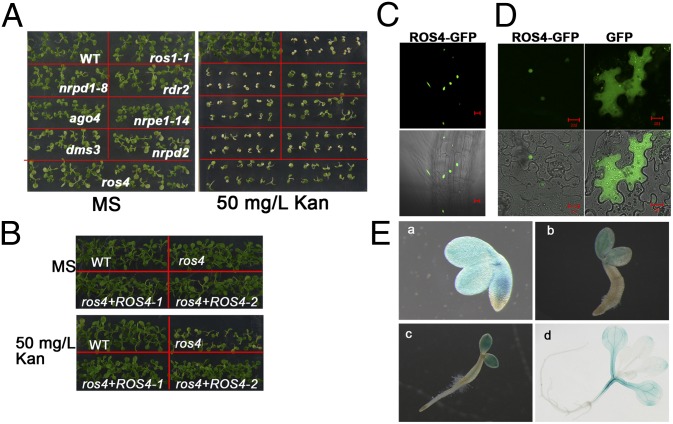
Fig. 1.
Analysis of kanamycin sensitivity of ros4 and other mutants and ROS4 expression. (A) Kan sensitivity of ros4 and RdDM pathway mutants. The seeds of ros1-1, nrpd1-8, rdr2, ago4, nrpe1-14, dms3, nrpd2, and ros4 were germinated on MS medium or MS medium supplemented with 50 mg/L Kan for 7 d. (B) Complementation of the ros4 mutant. A DNA fragment containing the ROS4 promoter (−2499 to −1) driving ROS4 full-length cDNA was transformed into the ros4 mutant. Two independent lines were tested for Kan sensitivity on 50 mg/L Kan MS medium. (C) ROS4-GFP localization in a root of a transgenic line carrying 35S::ROS4-GFP. (Upper) GFP fluorescence image. (Lower) GFP image combined with bright field. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (D) ROS4-GFP localization in a transient assay using tobacco leaves expressing 35S::ROS4-GFP (Left). GFP was used as a control (Right). (Upper) GFP fluorescence image. (Lower) GFP image combined with bright field. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (E) The expression analysis of ROS4 promoter::GUS in a transformed line at 12 h (a), 36 h (b), 48 h (c), and 14 d (d) after seed imbibition.