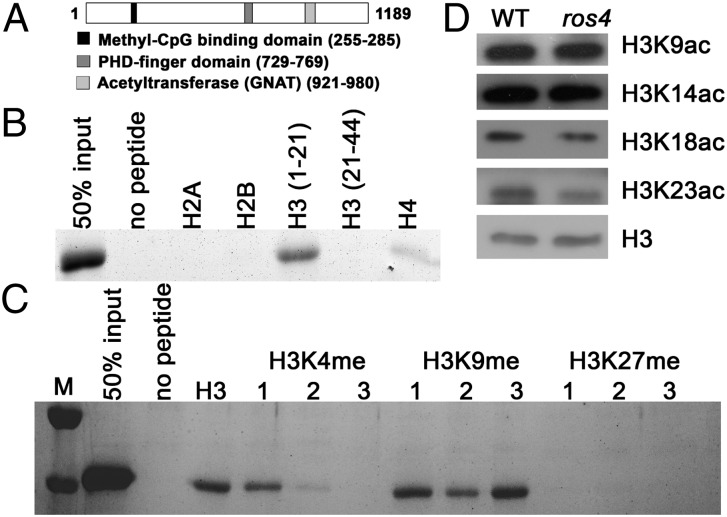
Fig. 2.
PHD domain of ROS4 binds to H3K4me0, and the mutation in ROS4 leads to reduction of acetylation of H3K18 and H3K23. (A) Structural diagram of the ROS4 protein. (B) In vitro assays of the binding of the recombinant PHD domain to unmodified histone peptides. H3 was divided into two fragments, H3 (1–21) and H3 (21–44). Note that the PHD domain also weakly binds to H4. (C) Effect of histone methylation on the binding of the PHD domain to the H3 tail. At least three independent experiments were done with similar results. (D) H3K9ac, H3K14ac, H3K18ac, and H3K23ac levels in the wild type and ros4. Total histone proteins were extracted from 5- to 7-d-old seedlings, and different antibodies were used for Western blotting; H3 was used as a loading control. M, size markers.