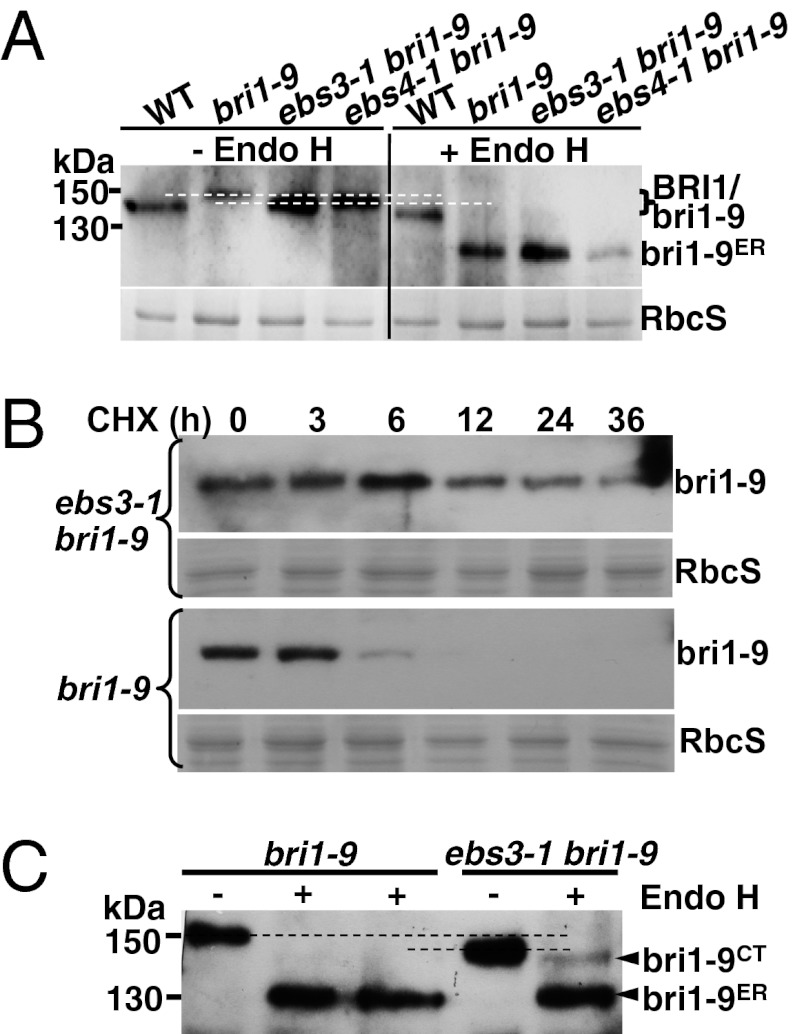
Fig. 1.
ebs3-1 mutation inhibits the ERAD of bri1-9. (A) Immunoblot analysis of bri1-9 in ebs3-1 bri1-9. (B) Immunoblot analysis of bri1-9 stability in bri1-9 and ebs3-1 bri1-9. (C) Endo H analysis of bri1-9 in bri1-9 and ebs3-1 bri1-9. For A and C, total proteins from 4-wk-old leaves were treated with or without Endo H, separated by SDS/PAGE, and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-BRI1 antibody. Equal amounts of total proteins were used in A, whereas five times more proteins in bri1-9 than ebs3-1 bri1-9 were used in C, which also contains technical duplicates of Endo H-treated bri1-9 samples. For B, 3-wk-old seedlings were transferred from 1/2 MS-agar medium into liquid 1/2 MS medium containing 180 μM CHX. Equal amounts of seedlings were removed at different time points to extract total proteins into 2× SDS sample buffer, which were subsequently separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-BRI1 antibody. The numbers on the left in A and C indicate molecular mass, bri1-9ER denotes Endo H-sensitive form, and bri1-9CT represents bri1-9 carrying C-type N-glycans. Dashed lines in A and C show the mobility difference between the bri1-9 band in bri1-9 and that of ebs3-1 bri1-9. Coomassie blue staining of the small subunit of Rubisco (RbcS) serves as the loading control.