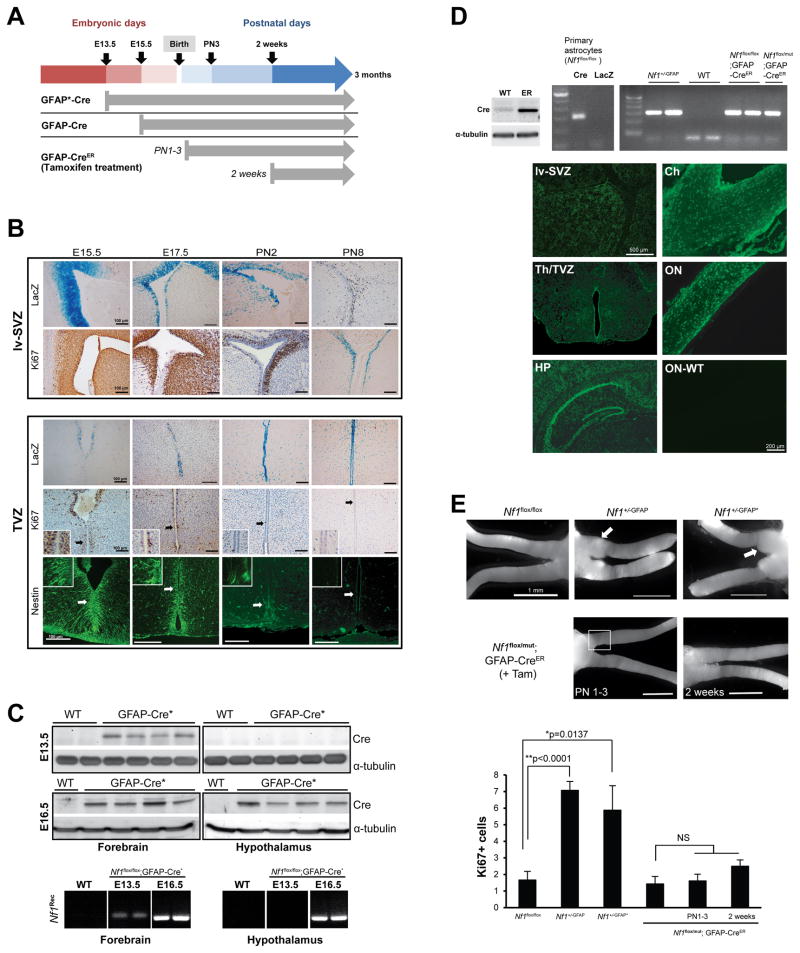
Figure 4. Embryonic Nf1 inactivation is required for optic glioma formation.
(A) The timing of Nf1 inactivation by Cre-mediated excision is shown for each strain. (B) X-gal staining reveals GFAP-Cre transgene expression in the lv-SVZ and TVZ beginning at E15.5. Whereas lv-SVZ cells are Ki67+ from E15.5 through PN8, scant numbers of Ki67+ or nestin+ cells are detected in the TVZ by PN2. (C) Cre expression and Nf1 gene recombination (Nf1Rec) is detected by E13.5 in the anterior forebrain/lv-SVZ (“forebrain”) and by E16.5 in the hypothalamus/TVZ (“hypothalamus”) of GFAP-Cre* mice. (D) Cre-mediated Nf1 gene recombination (PCR) in Nf1+/−GFAP mice and in tamoxifen-treated Nf1flox/flox; GFAP-CreER and Nf1flox/mut; GFAP-CreER mice was seen. Wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mouse brain was used as a negative control, whereas Ad5Cre-infected (Cre) and Ad5LacZ-infected (LacZ) Nf1flox/flox astrocytes served as positive and WT controls, respectively. Cre-ER fusion protein (~70 KDa) expression was detected in GFAP-CreER (ER), but not in WT, mouse brains. EGFP was expressed in tamoxifen-treated ROSA-GREEN; GFAP-CreER mouse brains and optic nerves at 1 month of age, but not in a WT mouse optic nerve (ON-WT). HP: hippocampus, Th: thalamus, Ch: chiasm, ON: optic nerve. (E) Whereas optic gliomas develop in Nf1+/-GFAP and Nf1+/-GFAP* mice, no gliomas formed in Nf1flox/flox or Nf1flox/mut; GFAP-CreER treated with tamoxifen (+Tam) beginning at PN1 or PN14. Increased Ki67+ cells were found in the prechiasmatic and chiasmal regions (square) of Nf1+/−GFAP and Nf1+/−GFAP* mice. In contrast, the number of Ki67+ cells in Nf1flox/mut; GFAP-CreER postnatally-treated with tamoxifen is indistinguishable from control Nf1flox/flox mice. Values denote the mean ± SEM. See also Figure S3.