Abstract
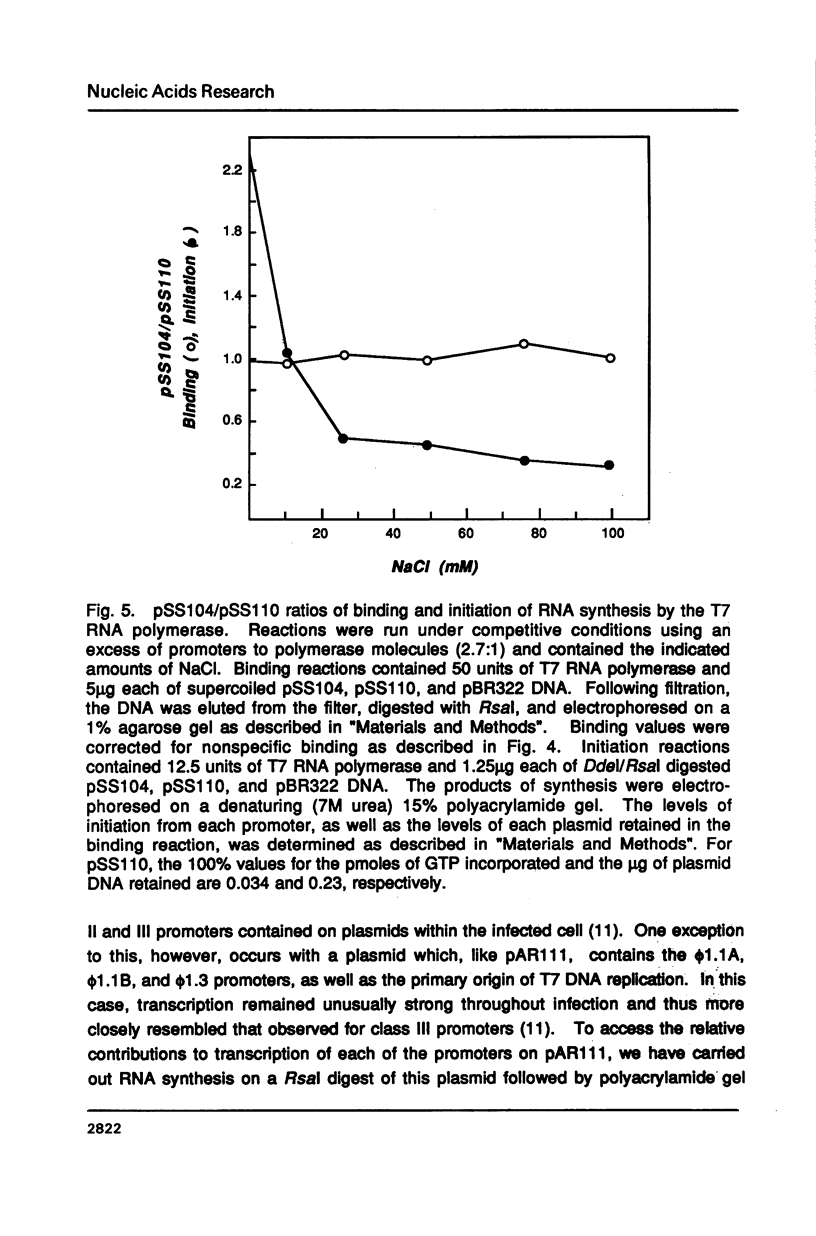
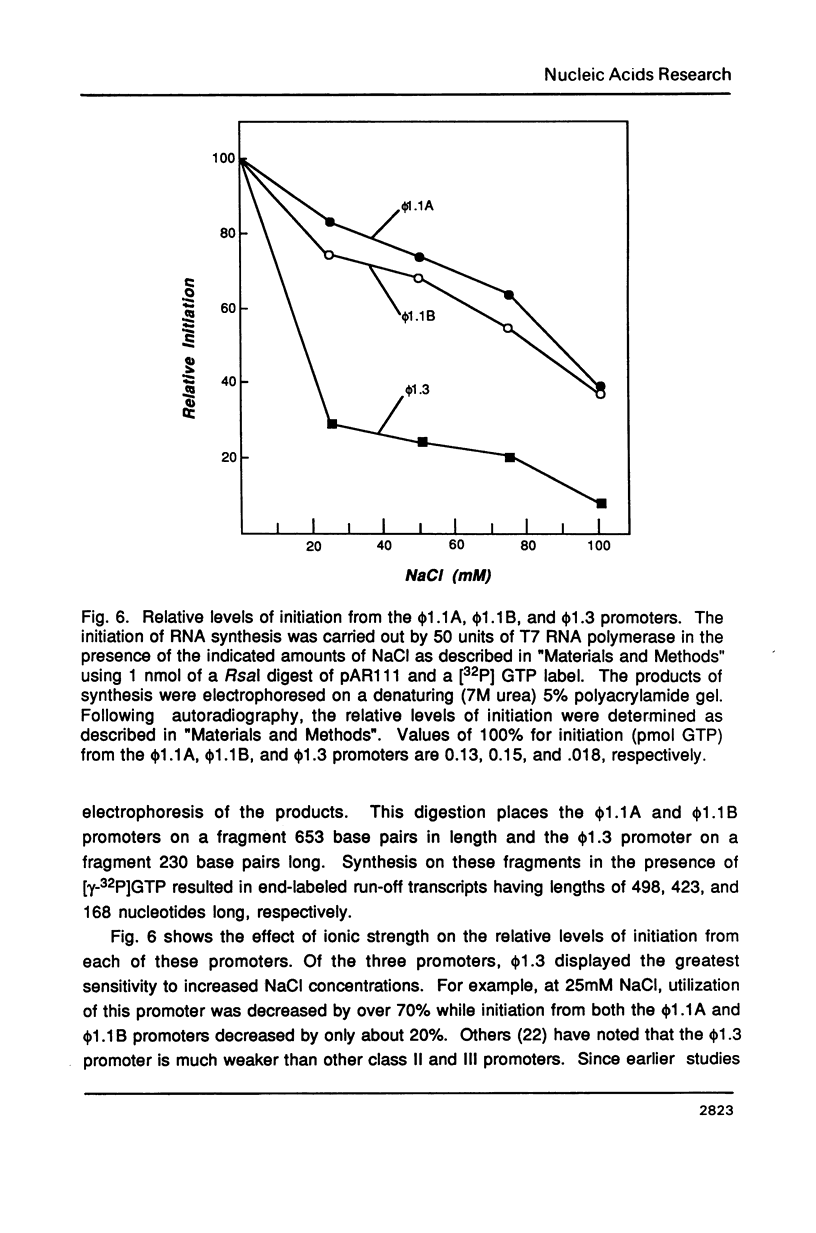
T7 RNA polymerase plays an important role in both the transcription and replication of bacteriophage T7. In this study we have used a nitrocellulose filter binding assay to examine the binding properties of the T7 RNA polymerase with T7 promoters cloned into plasmid DNAs. Promoter-specific binding was shown to be relatively insensitive to variations in the ionic strength of the incubation solution but dependent on the helical structure of the DNA. On the other hand, nonpromoter interior-site binding was independent of the superhelicity of the DNA but extremely sensitive to changes in the ionic strength. These results suggest that nonspecific binding results from ionic interactions between positively charged residues of the polymerase and the polyanionic backbone of the DNA, whereas promoter-specific binding is dependent upon base-specific contacts within the promoter sequence. A comparison between the transcriptional activity and binding strengths of the RNA polymerase to specific promoters indicates little correlation between these two properties. This suggests that differential promoter binding does not represent a major mechanism for regulating transcription in bacteriophage T7. Instead, factors which influence the efficiency or rate of formation of the polymerase-promoter open complex are found to have the major role in determining transcriptional levels in this system.
Full text
PDF




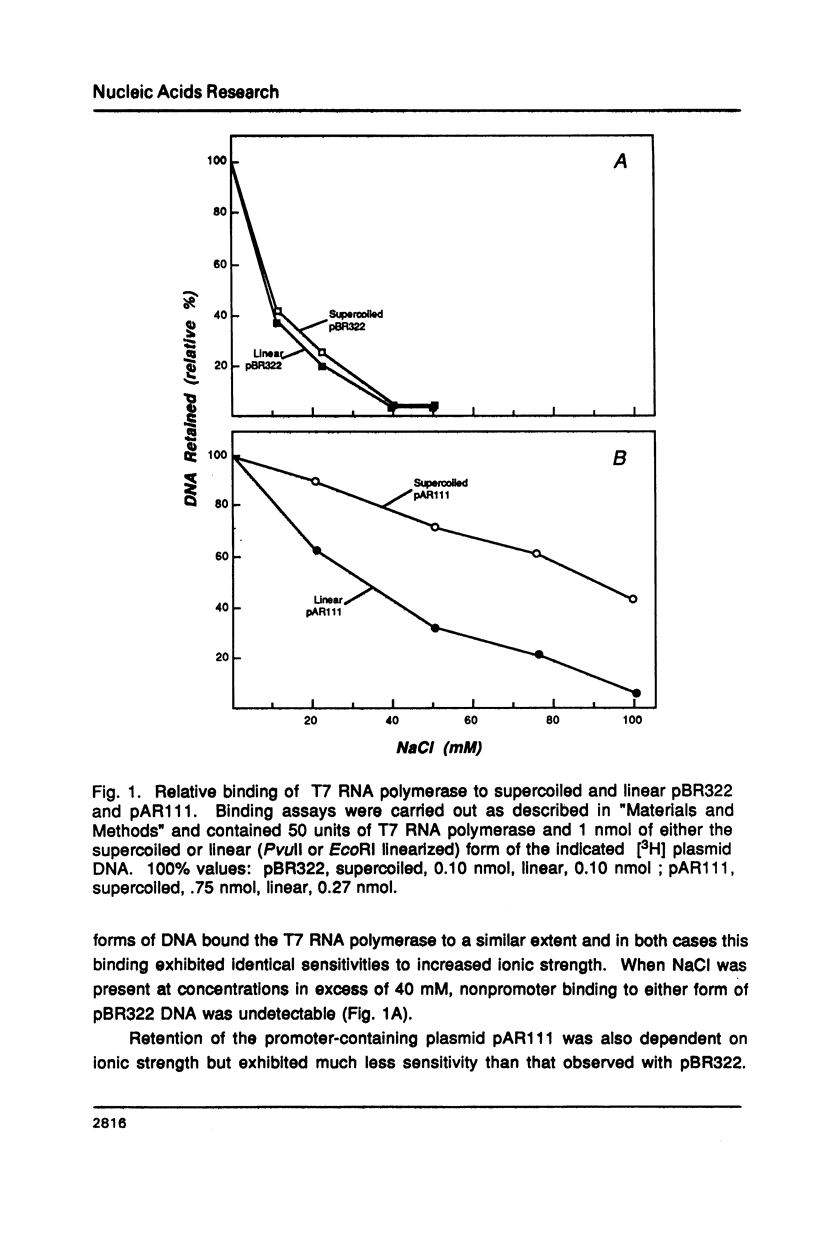
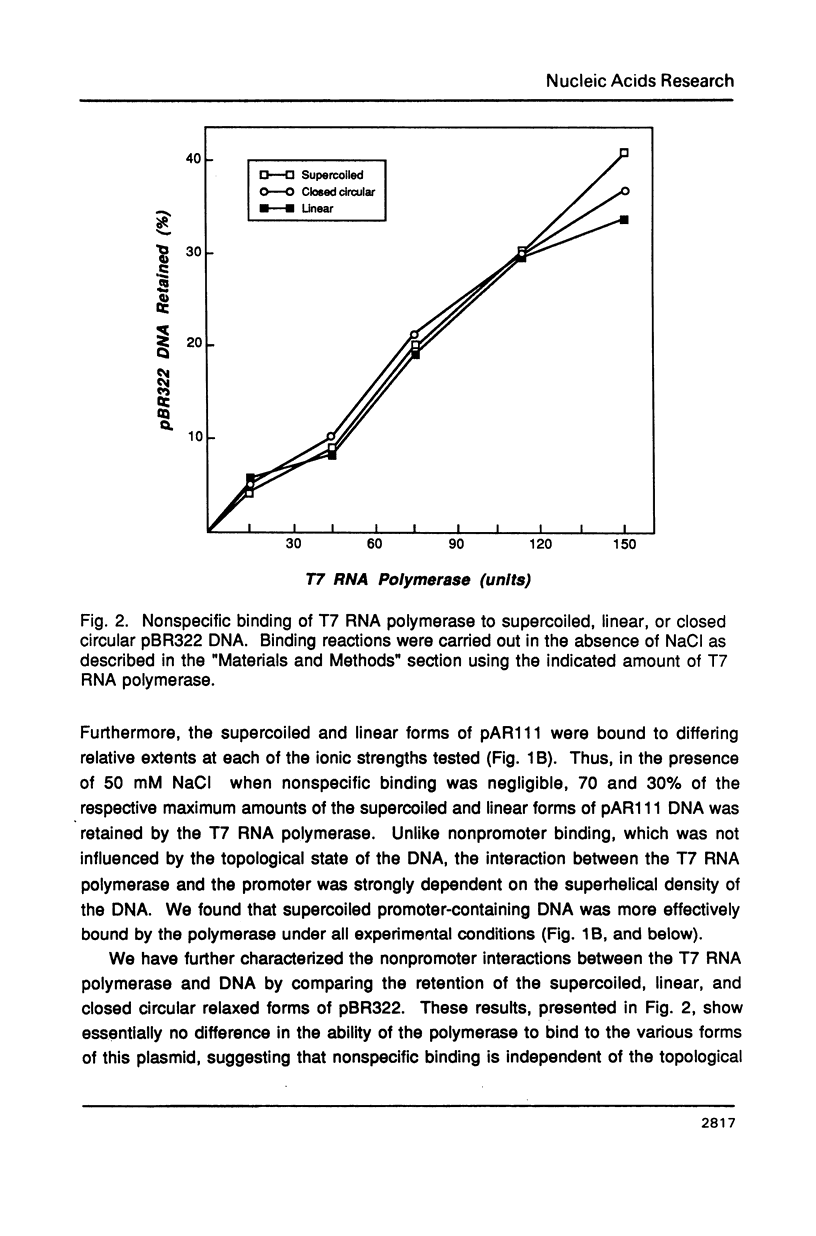
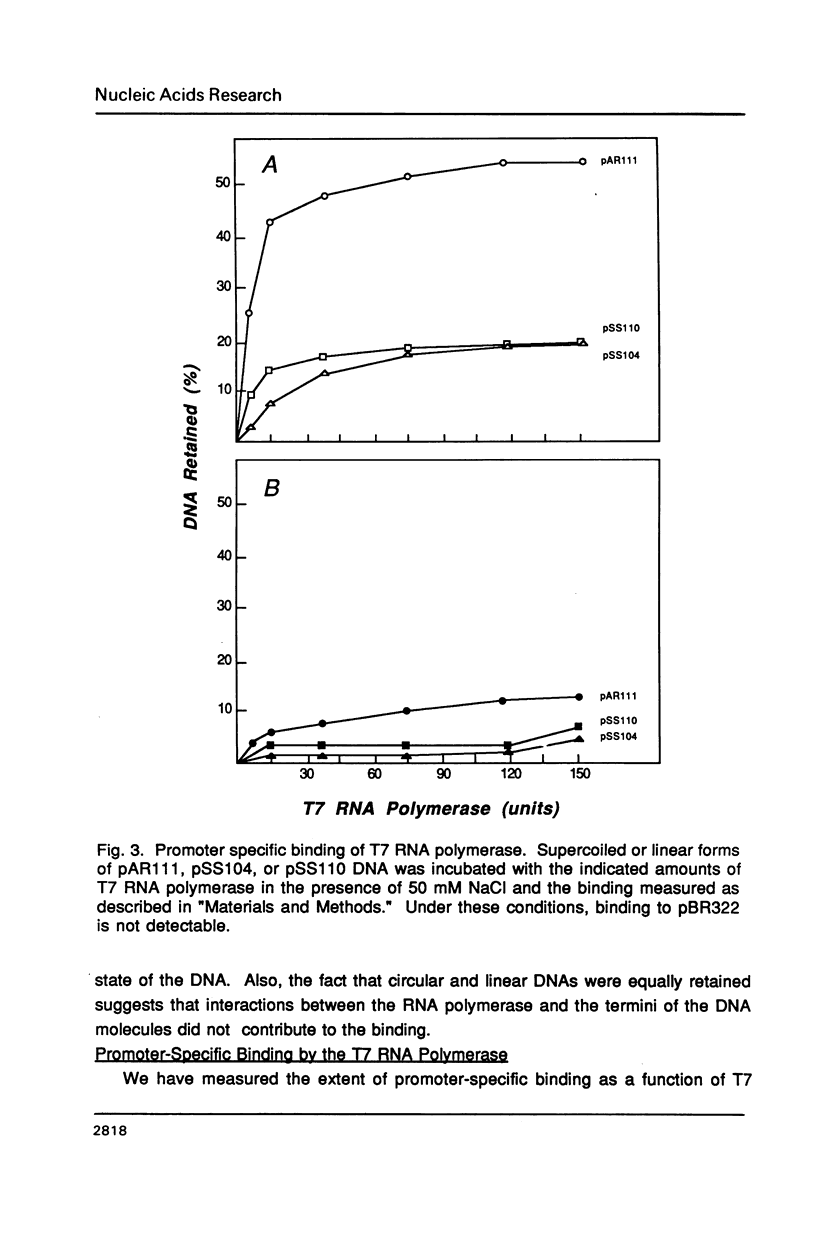

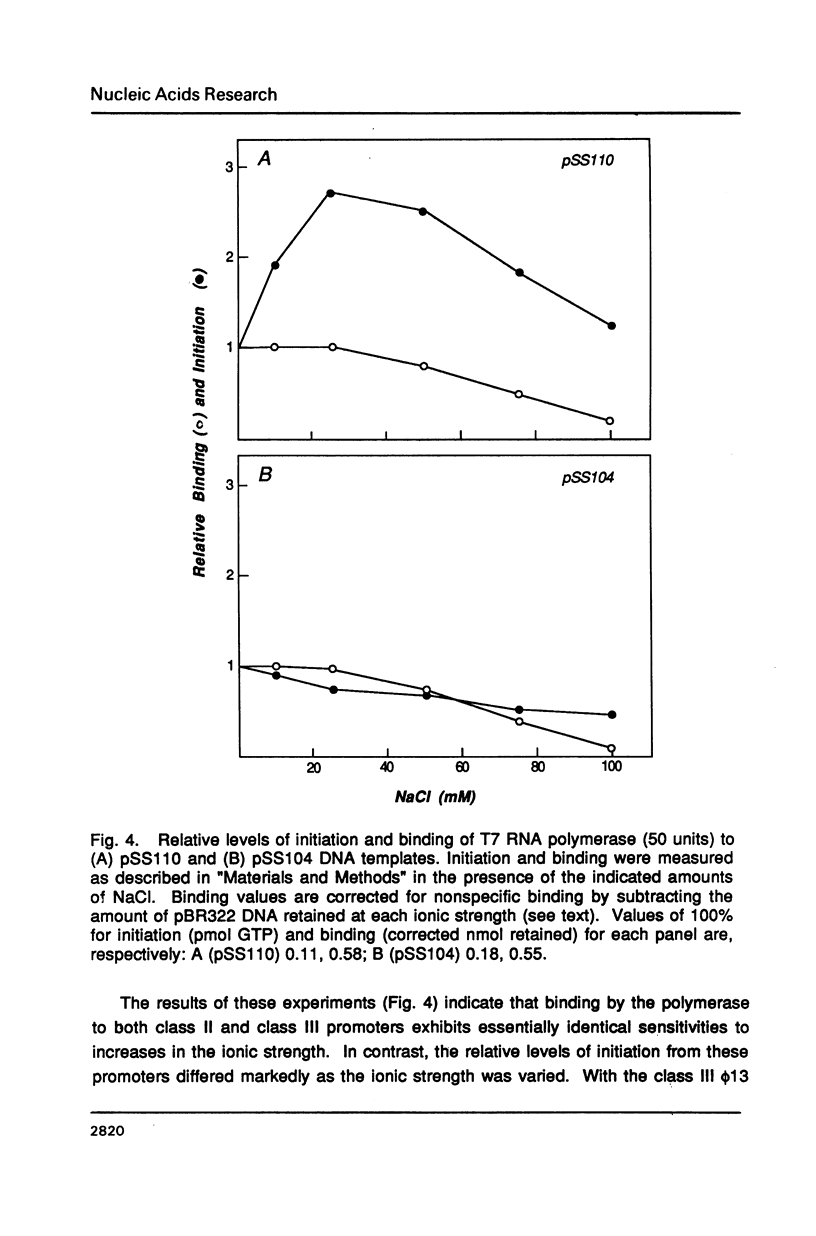





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. N., Klement J. F., McAllister W. T. Relationship between promoter structure and template specificities exhibited by the bacteriophage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C. F factor-mediated inhibition of bacteriophage T7 growth: increased membrane permeability and decreased ATP levels following T7 infection of male Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence from the genetic left end of bacteriophage T7 DNA to the beginning of gene 4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):303–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Hinkle D. C. Bacteriophage T7 DNA replication in vitro. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by T7 RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7956–7964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann R. Bacteriophage T7 genetics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1976;75:77–110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66530-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. The role of sigma subunit in site selection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):157–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C. Evidence for direct involvement of T7 RNA polymerase bacteriophage DNA replication. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):136–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.136-141.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe L. K., Carter A. D., McAllister W. T. Identification of a potential control region in bacteriophage T7 late promoters. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):653–656. doi: 10.1038/299653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Carter A. D. Regulation of promoter selection by the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4821–4837. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Morris C., Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W. Utilization of bacteriophage T7 late promoters in recombinant plasmids during infection. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Wu H. L. Regulation of transcription of the late genes of bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Recognition and initiation site for four late promoters of phage T7 is a 22-base pair DNA sequence. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):35–39. doi: 10.1038/280035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. The 5'-terminal nucleotides of T7 bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano L. J., Tamanoi F., Richardson C. C. Initiation of DNA replication at the primary origin of bacteriophage T7 by purified proteins: requirement for T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4107–4111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tabor S., Tamanoi F., Richardson C. C. Nucleotide sequence of the primary origin of bacteriophage T7 DNA replication: relationship to adjacent genes and regulatory elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3917–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss H. S., Boston R. S., Record M. T., Jr, Burgess R. R. Variables affecting the selectivity and efficiency of retention of DNA fragments by E. coli RNA polymerase in the nitrocellulose-filter-binding assay. Gene. 1981 Jan-Feb;13(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Organization and expression of bacteriophage T7 DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):999–1007. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H. Genetic and physical mapping of the late region of bacteriophage T7 DNA by use of cloned fragments of T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):503–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



