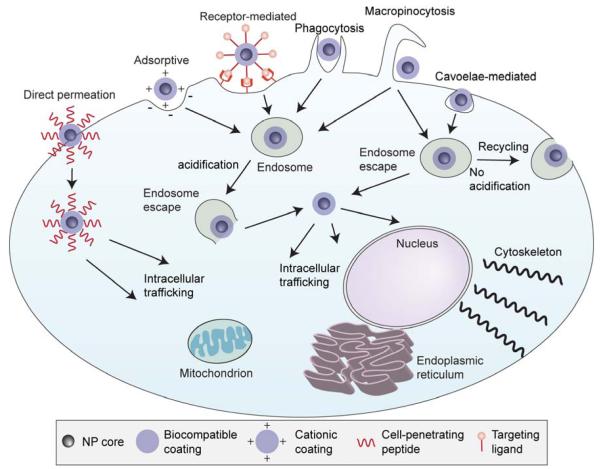
Figure 4.
Cellular barriers encountered by NPs. Entry into the cell across the cell membrane can occur by direct permeation, or by various types of endocytosis mechanisms. Upon endocytosis, the NP must escape the endosome before acidification degrades the payload or the NP is exocytosed with membrane recycling. After the NP gains access to the cytoplasm of the cell, intracellular trafficking will ensure that the therapeutic payload will reach the desired site of action such as the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus, or cytoskeleton.