Figure 4.
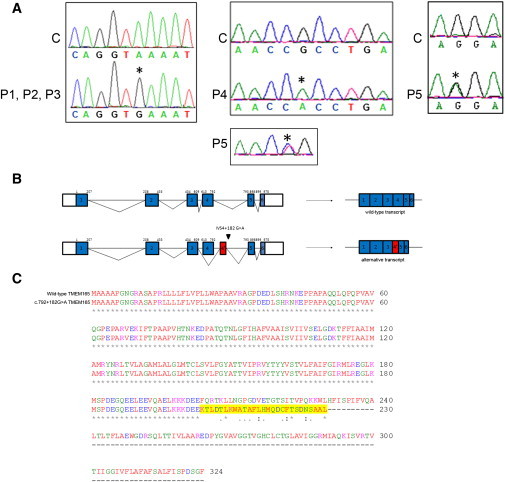
TMEM165 Mutations
(A) In the left panel is the sequence alignment of the genomic DNA fragment from a control C and cases P1, P2, and P3 homozygous for the G>A transition at position c.792+182. In the middle and right panels is the sequence alignment of the cDNA fragment from a control C and cases P4 and P5. P4 is homozygous for the G>A transition at position c.377, and P5 is compound heterozygous for the C>T transition at position 376 and the G>A transition at position 910. Nucleotides affected by the mutations and the predicted effects on protein length are indicated above each sequence.
(B) Schematic representation of the predicted genomic (top) and cDNA (bottom) structure of TMEM165 in the control and cases P1, P2, and P3. Coding exons are shown in blue boxes, and introns (not drawn to scale) are represented by lines. The beginning and end of the open reading frame are labeled; the numbering above each exon is based on coding nucleotides. The red box represents the alternative exon 4 (4′) used in cases P1, P2, and P3.
(C) Predicted effect of the c.792+182G>A mutation on TMEM165. Sequence alignment was compared between wild-type TMEM165 and mutant TMEM165. The amino acids that changed as a result of the mutation are highlighted in yellow. The mutated TMEM165 is truncated and shortened by 94 amino acids.
