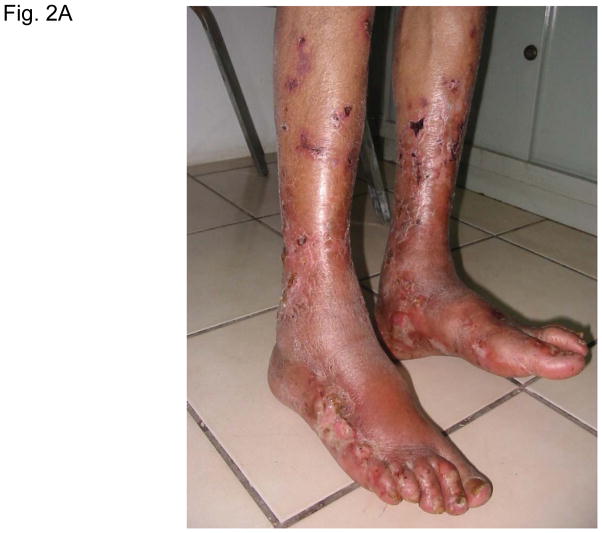
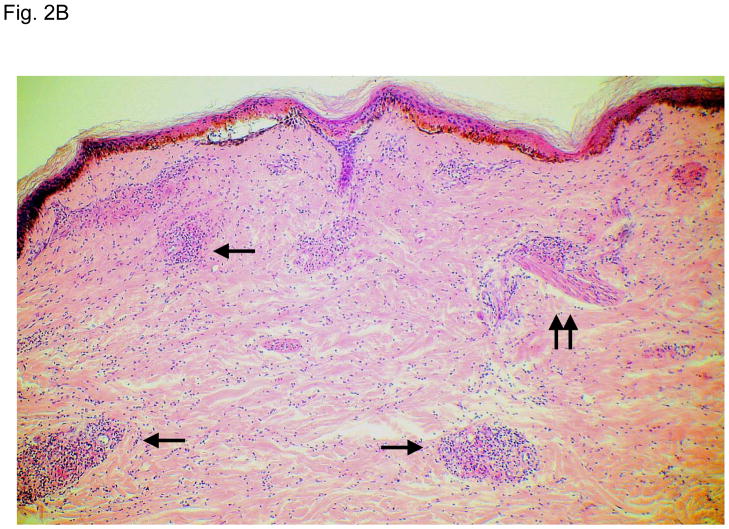
Figure 2. Typical skin lesions and underlying histopathology of diffuse lepromatous leprosy caused by M. lepromatosis.
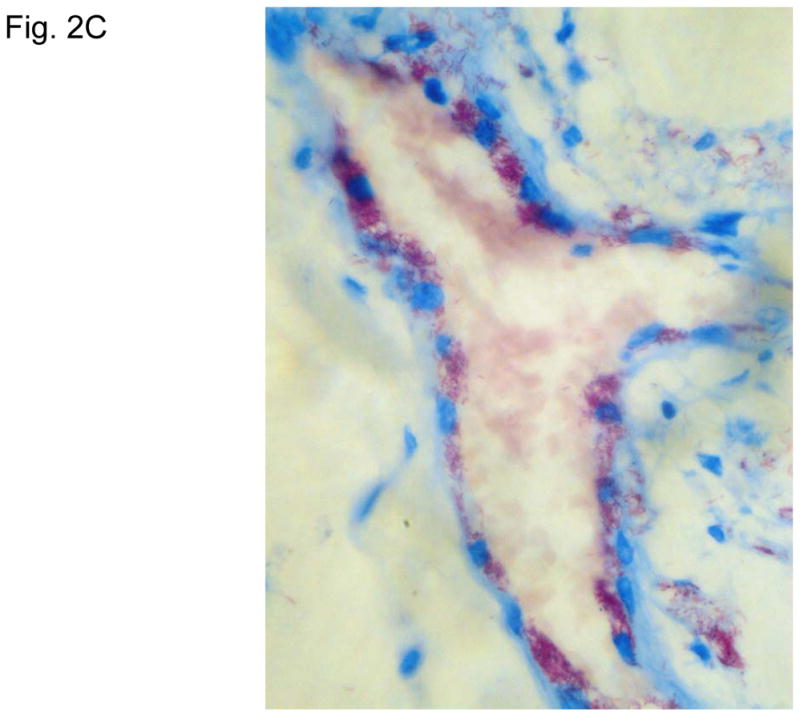
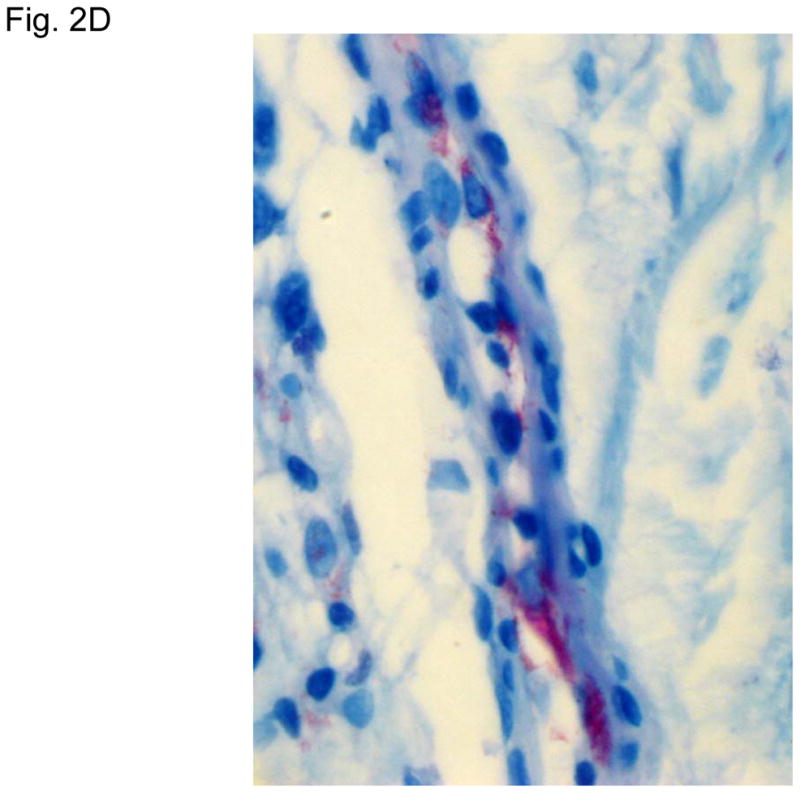
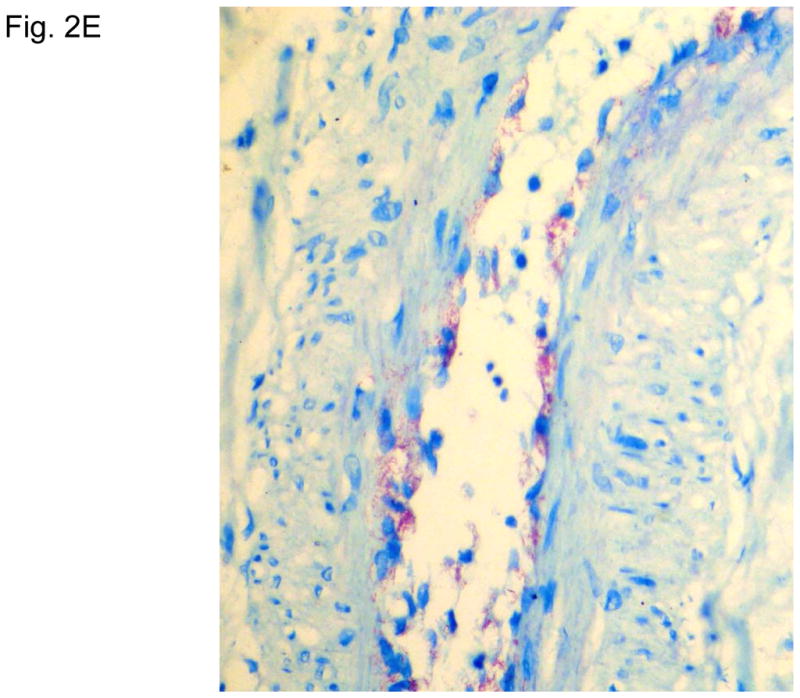
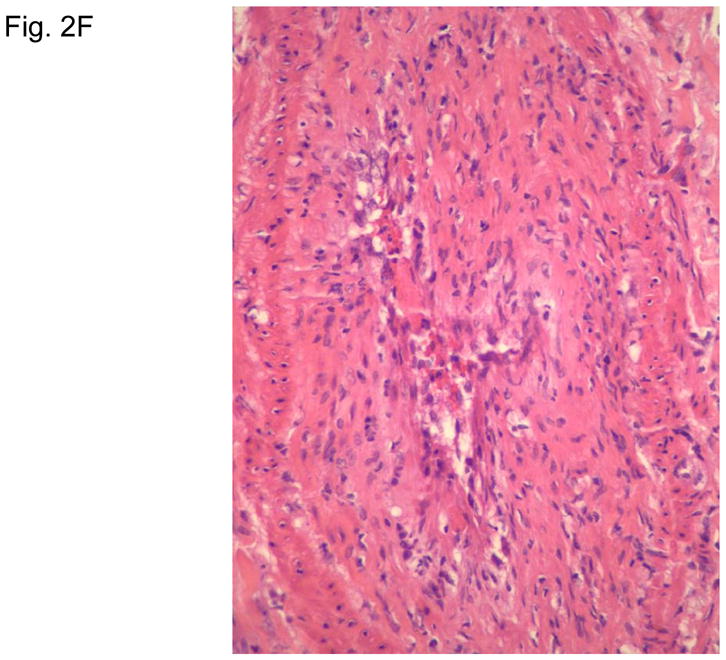
A. Advanced skin ulcers, eschars, and edema in the legs and feet. B. Epidermal necrosis and diffuse cutaneous inflammatory infiltration with leukocytoclastic vasculitis (arrows) and neuritis (dual arrows) (H & E, 35x). CDE. Invasion of the mycobacterium, as highlighted by red-colored bacilli, into the endothelia of a vein, arteriole, and medium artery respectively (Fite, 400x). E. Also endothelial proliferation. F. End stage occlusion of a medium artery (H & E, 100x).