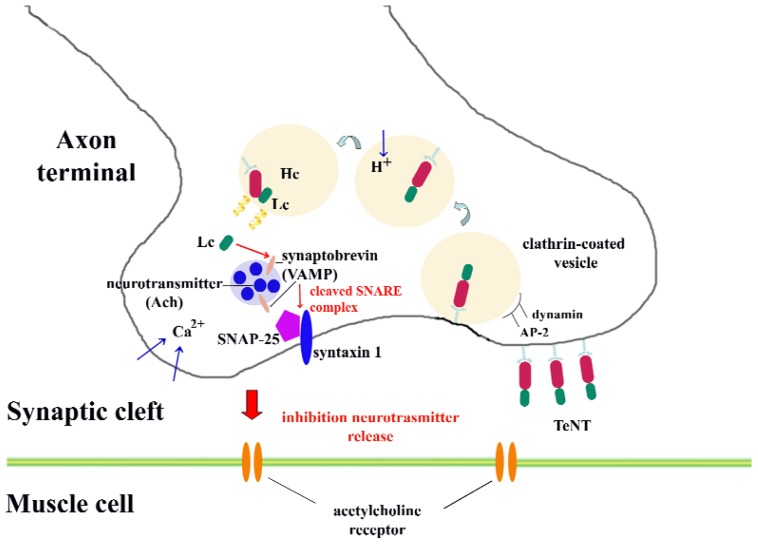
Figure 2.
Proposed internalization pathway of tetanus toxin. The ganglioside-recognition domain in the C-terminal region of HC allows the toxin to be internalized into the neuron. The light chain of the toxin (LC) cleaves the soluble NSF attachment receptor (SNARE) complex, inhibiting neurotransmitter release.