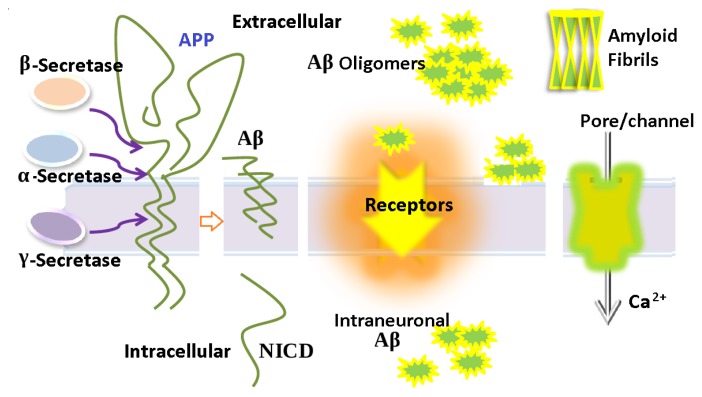
Figure 4.
The cleavage of APP by α-, β- and γ-secretase and the production of Aβ peptides are shown on the left side of the figure. The following toxic mechanisms are illustrated in the figure: formation of Aβ oligomers and its further conversion to fibrils; disruption of membrane receptors; adsorption on membrane surface which alters the property of the membrane; formation of pore which causes the leakage of Ca2+; and the accumulation of intraneuronal Aβ.