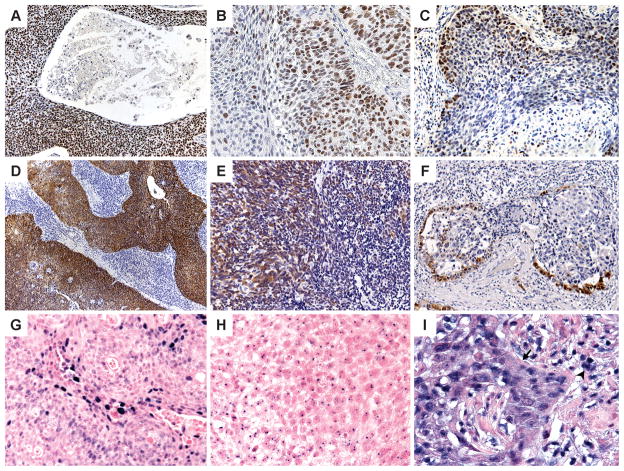
Figure 1.
ProExC immunohistochemistry: Staining of >95% (A) and 50% (B) of the tumor; staining of less than 33% of the tumor cells (C) is defined as negative. p16 immunohistochemistry: 90% (D), 50% (E) and 10% (F) strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining of the tumor. HPV in situ hybridization: Positive HPV ISH can appear as diffuse (F) and/or punctate (G) nuclear reactivity; high background (H) can lead to staining of lymphocytes (arrowhead) and punctate staining that extends beyond the tumor nucleus and into the cytoplasm.