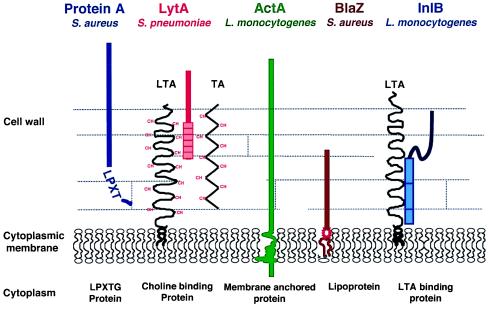
Figure 1.
Major types of surface proteins in Gram-positive bacteria. Protein A, an immunoglobulin-binding protein, is covalently linked to the cell wall and exposed on the cell surface. The amidase LytA is loosely attached to choline (CH) residues decorating teichoic acid (TA) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) in Streptococcus pneumoniae (4). The actin-polymerizing protein ActA of Listeria monocytogenes is membrane-anchored and exposed to the medium (7). The β-lactamase BlaZ encoded by the resistance plasmid PI258 of Staphylococcus aureus is associated to the membrane and partially released into the medium (8). InlB of L. monocytogenes is loosely attached to LTA (5, 6). It is weakly exposed on the cell surface.