FIGURE 7.
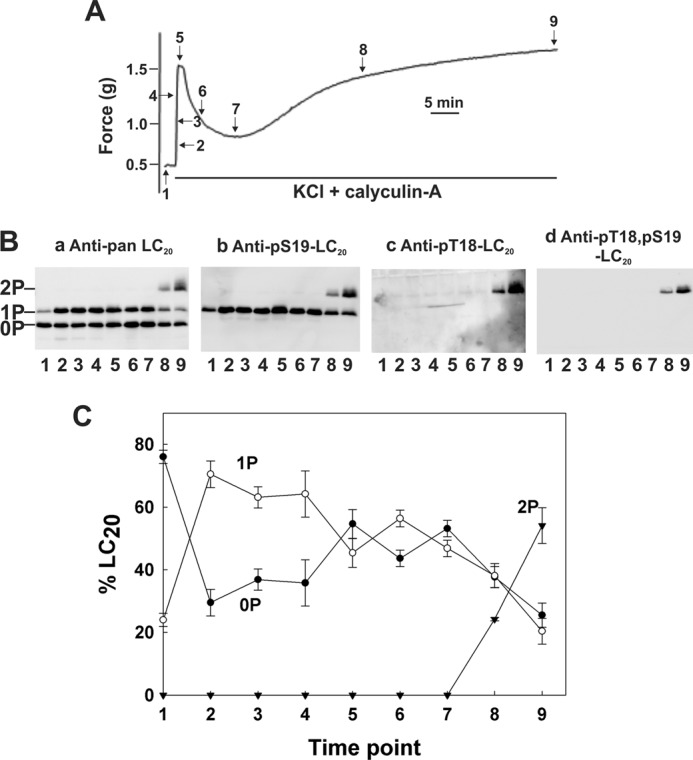
Contraction and LC20 diphosphorylation in intact rat caudal arterial smooth muscle in response to KCl and calyculin-A in the presence of extracellular Ca2+. A, membrane-intact rat caudal arterial smooth muscle strips, mounted on a force transducer in Ca2+-containing H-T buffer, were treated with KCl (87 mm) and calyculin-A (0.5 μm). Separate tissues were harvested at the indicated times during the contraction for analysis of LC20 phosphorylation by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and Western blotting (B) with antibodies to LC20 (panel a), Ser(P)19-LC20 (panel b), Thr(P)18-LC20 (panel c), and Thr(P)18,Ser(P)19-LC20 (panel d). Numbers below the gel lanes correspond to the time points in A. C, cumulative quantitative data showing the proportions of unphosphorylated (0P, closed circles), mono- (1P, open circles), and diphosphorylated LC20 (2P, closed inverted triangles) as a function of time. Values represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 3).
