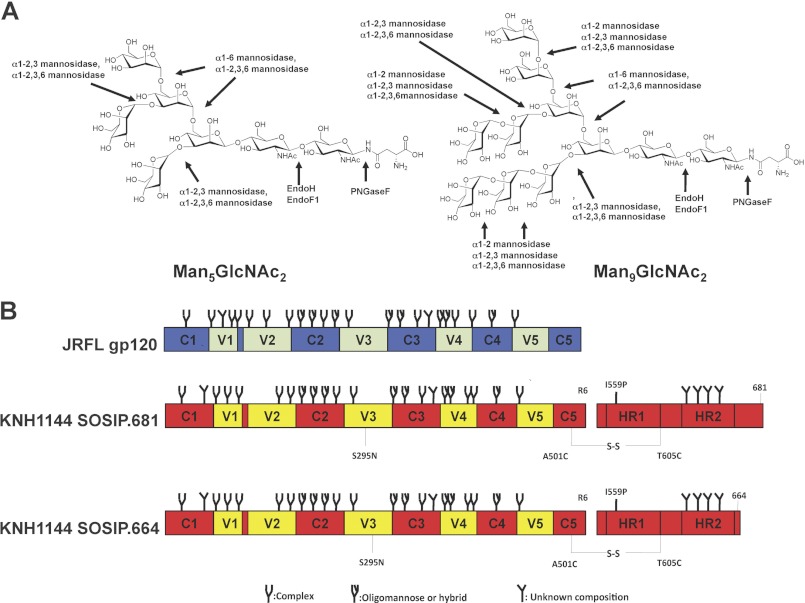
FIGURE 1.
Schematics of Env constructs and glycosidase specificities. A, two different oligomannose N-glycans (Man5GlcNAc2 and Man9GlcNAc2) that are present on Env proteins produced in GnTl−/− cells are depicted, along with the cleavage sites for the enzymes used in this study. Env produced in the presence of kifunensine would only contain Man9GlcNAc2 glycans. B, schematics of the gp120 and gp140 proteins. JR-FL gp120, conserved regions in blue, variable regions in green; KNH1144 gp140, conserved regions in red, variable regions in yellow. The gp140 was modified to reconstitute the 2G12 epitope (S295N substitution), and the 2F5 and 4E10 epitopes in the MPER (A662E, G664D, S668N, and N671T substitutions) (47). The gp140 also contains the A501C and T605C substitutions to create the SOS disulfide bond between gp120 and gp41 (44), the I559P mutation to promote trimerization (45), and a hexa-arginine cleavage site (R6) to enhance cleavage efficiency (54). The type of N-glycan indicated to be present at each glycosylation site (oligomannose, complex or undefined) is based on glycan characterization of IIIB gp120 (83). However, which type of glycan is actually present at some of these sites may vary between strains (83), and can also depend on the oligomerization status of Env proteins (69, 84). The gp41 glycans have not been characterized.