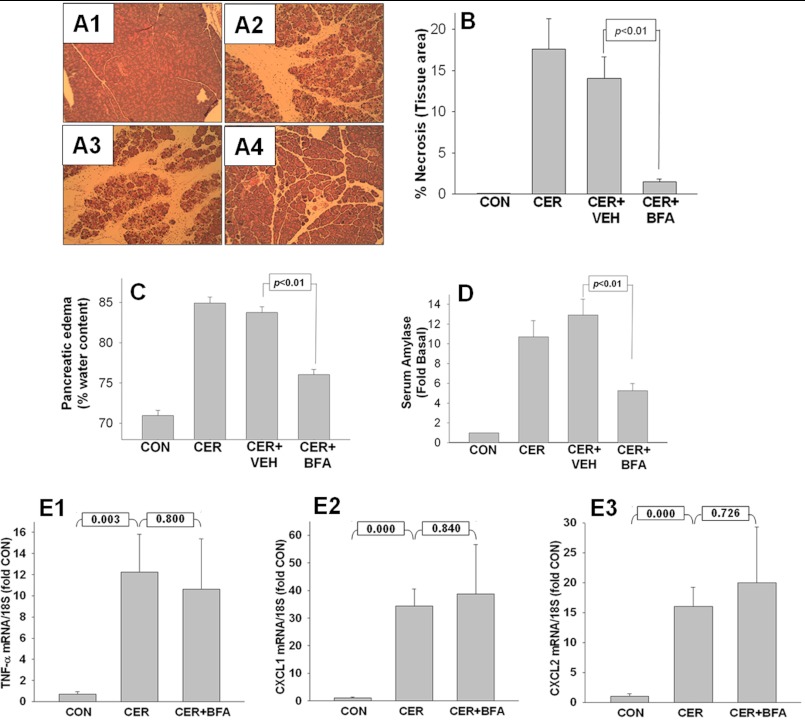
FIGURE 4.
BFA reduces severity of CER-induced pancreatitis without affecting inflammatory cytokine up-regulation. A1–A4, BFA reduces pancreatic necrosis. Pancreatic tissue from control mice (A1), mice with 10-h CER-induced pancreatitis (A2), and mice pretreated either with vehicle (A3) or with BFA (A4) was dissected for histology and quantified for the amount of necrotic cell death per total area of pancreatic tissue. Representative images are shown. B, histograms from quantified histology data described in A1–A4 show the decrease (p < 0.01) in the amount of necrotic area in mice treated with BFA relative to vehicle control (CON). VEH, vehicle. C and D, BFA reduces pancreatic edema (C) and serum amylase (D) at the end of 10 h of pancreatitis. E1–E3, BFA does not decrease the severity of pancreatitis by interfering with the transcriptional regulation of TNF-α (E1), CXCL1 (E2), or CXCL2 (E3) in the pancreas. Histograms represent the -fold increase in the amount of TNF-α, CXCL1, and CXCL2 transcripts relative to control as assessed by real-time PCR.