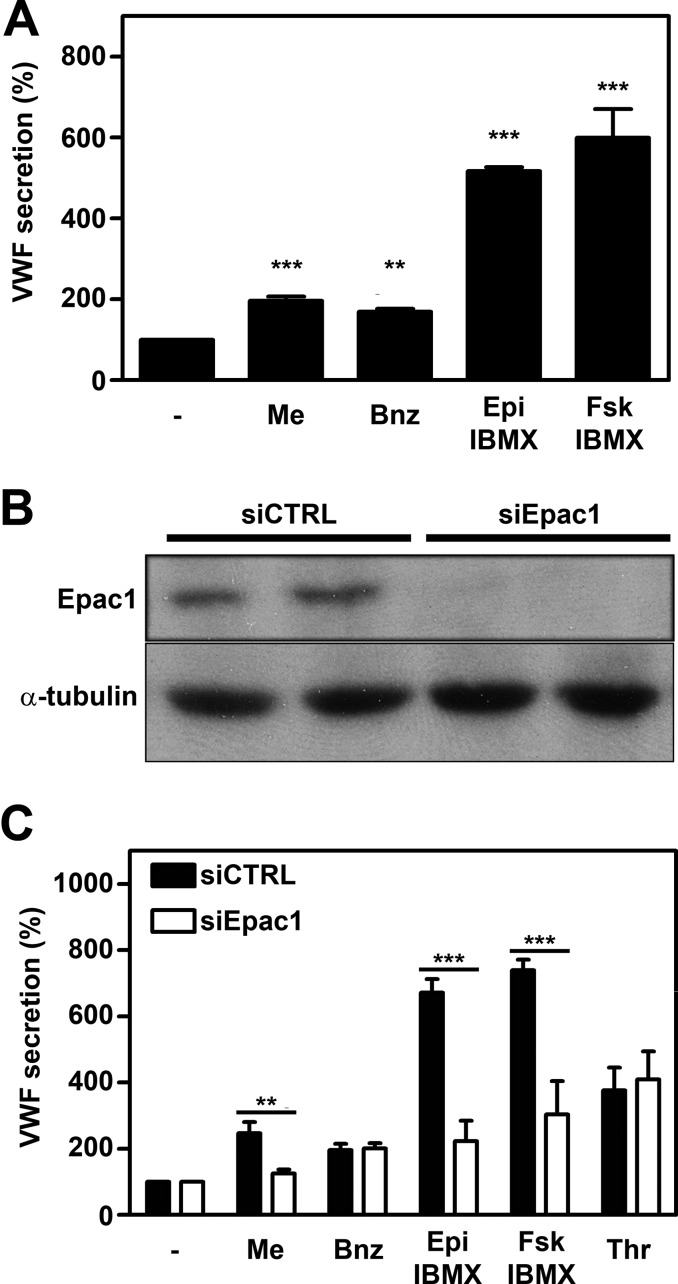
FIGURE 1.
Involvement of Epac in cAMP-mediated WPB release. A, HUVECs were incubated with SF medium (−), supplemented with 1 μm Me-cAMP-AM (Me), 1 μm 6-Bnz-cAMP-AM (Bnz), 10 μm epinephrine and 100 μm IBMX (Epi), or 10 μm forskolin and 100 μm IBMX (Fsk). After 60 min, the amount of VWF secreted in the medium was measured by ELISA. Basal VWF secretion (unstimulated) was set to 100%. (n = 5, ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett post hoc test.) Error bars show S.E. B, HUVECs were transfected with a control siRNA SMARTpool (siCTRL) or an siRNA SMARTpool targeting Epac1 (siEpac1). Western blot analysis at 72 h post-transfection showed down-regulation of Epac1 expression. Levels of α-tubulin are shown as a protein loading control. C, siCTRL- and siEpac1-treated HUVECs were incubated for 60 min with SF medium (−), supplemented with 1 μm Me-cAMP-AM (Me), 1 μm 6-Bnz-cAMP-AM (Bnz), 10 μm epinephrine and 100 μm IBMX (Epi), 10 μm forskolin and 100 μm IBMX (Fsk) or 1 unit/ml thrombin (Thr). The amount of VWF secreted in the medium was measured by ELISA. Unstimulated VWF secretion was not affected by the treatment and was set to 100%. (n = 3; ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test for selected comparison.) Error bars show S.E.