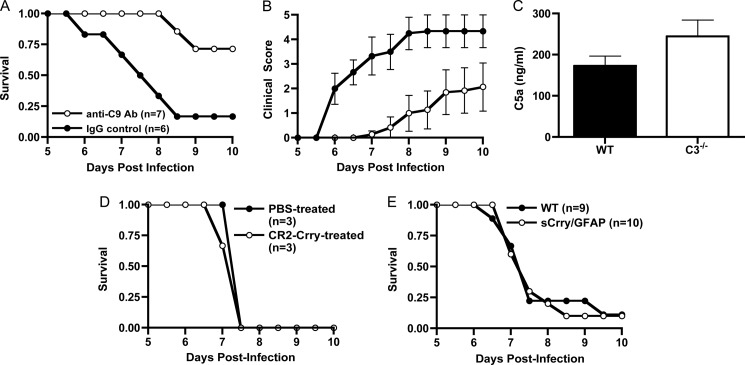
FIGURE 2.
Terminal pathway activation occurs in C3−/− mice in ECM. Wild type mice were injected with 5 × 105 PbA-iRBC as described under “Experimental Procedures” A, anti-C9 antibody (Ab)-treated mice were significantly protected from ECM (p = 0.0001, log rank test) and had reduced clinical scores (B) as compared with mice treated with isotype control antibody (p < 0.05 on days 6–9, Wilcoxon rank sum test). C, wild type (n = 8) and C3−/− mice (n = 5) were injected with PbA-iRBC as in A. On day 6 after infection, mice were bled, and serum C5a levels were determined by ELISA. C5a levels in C3−/− mice were elevated, but not significantly, as compared with wild type mice. D, treatment of wild type mice with CR2-Crry (100 μg, n = 3) on days 5 and 6 did not significantly alter the course of ECM as compared with PBS-treated mice (n = 3). E, sCrry/GFAP mice (n = 10) were fully susceptible to disease-induced mortality as compared with wild type mice (n = 9).