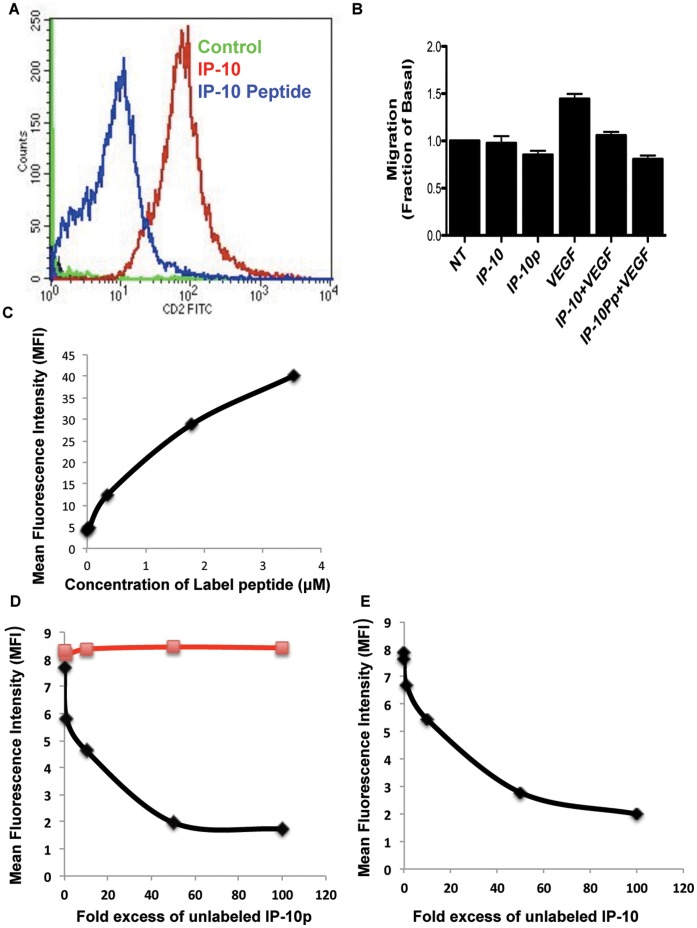
Figure 2. Binding of IP-10p to HMEC cells occurs via CXCR3.
A) Biotin tagged IP-10 and IP-10p were incubated with cells and then probed with FITC-conjugated with streptavidin and analyzed on a BD FACSCalbur flow cytometer. Control cells were incubated with FITC-Streptavidin alone. Motility analysis shows the effects of biotinylated IP-10 (23.2 µM), IP-10p (10 µM) C) Binding of IP-10p to endothelial cells is saturable. Endothelial cells were incubated with increasing doses of IP-10p as indicated. Cells were extensively washed in PBS with FITC-Streptavidin analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean fluorescent intensities of labeled cells are plotted against the concentrations of IP-10p. D) IP-10p binds specifically to endothelial cells. Endothelial cell were incubated with 1ug/ml biotin labeled IP-10p and increasing control of unlabeled IP-10p or scrambled control at peptide. Cells were stained with FITC-Streptavidin analyzed by flow cytometry. (µg unlabeled IP-10p ν unlabeled scrambled peptide) E) IP-10 competes with IP-10p for binding. Endothelial cells were incubated with 1ug/ml biotin labeled IP-10p and IP-10. Cells were stained with FITC-Streptavidin analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean fluorescent intensities are plotted as a function of increasing quantities of competitor proteins. Data shown are of N = 6.