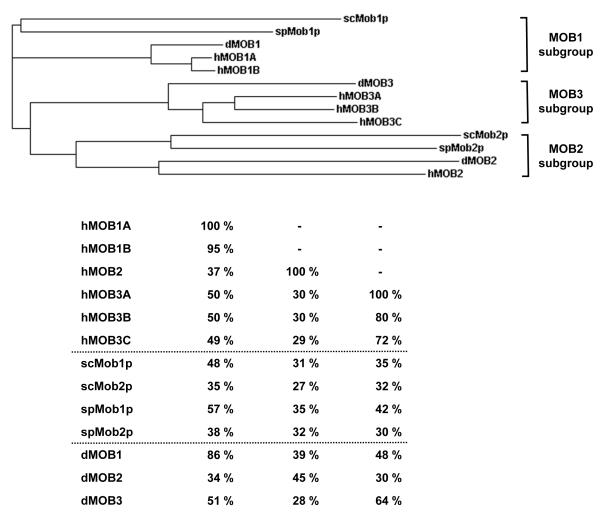
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationships within the MOB protein family.
Top: Phylogenetic tree using Clustal W phylogenetic calculation based on the neighbour-joining method. Budding and fission yeast scMob1p and spMob1p, respectively, group together with dMOB1 and hMOB1A/B (MOB1 subgroup), while scMob2p and spMob2p fall into a group together with dMOB2 and hMOB2 (MOB2 subgroup). dMOB3 together with hMOB3A/B/C forms a third group (MOB3 subgroup). Bottom: Display of primary sequence identities within the MOB protein family. hMOB1 is closest related to scMob1p, spMob1p, and dMOB1 in the respective species. hMOB2 is not as well conserved as hMOB1, since it aligns similarly with several MOB proteins in yeast and flies. The MOB3 subgroup displays close identity between dMOB3 and hMOB3A/B/C.