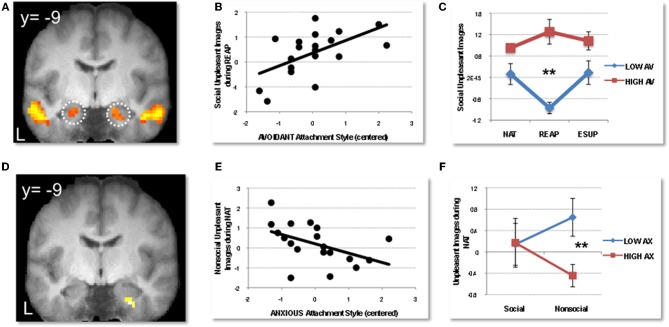
Figure 3.
Modulation of social emotion perception and regulation by adult attachment style. Adapted from Vrticka et al. (2012a). (A) Bilateral amygdala activation to social (versus nonsocial) emotional scenes perception, regardless of valence (positive or negative) and task. (B) Positive correlation between avoidant attachment (AV) scores and activity in left amygdala for social negative images during reappraisal (averaged across voxels). (C) Median split illustrating data for high (red; N = 5) versus low (blue; N = 8) avoidantly attached participants in left amygdala, showing a decrease in activity to social negative images during reappraisal for the low but not high avoidant group (**indicate the differential response accounting for significant effects in the correlation analysis). (D) Right amygdala activation to negative scenes showing a significant modulation by anxious attachment (AX) scores during natural viewing conditions. (E) Negative correlation between anxious attachment scores and response to nonsocial negative scenes in the right amygdala. (F) Median split illustrating data for high (red; N = 8) versus low (blue; N = 9) anxiously attached participants in right amygdala, showing that activation to negative scenes was greater for nonsocial content in those with lower AX scores, but greater for social content in those with higher AX scores. (**indicate the differential response accounting for significant effects in the whole-brain correlation analysis). NAT = natural viewing, REAP = reappraisal, ESUP = expressive suppression. BOLD signal is depicted in arbitrary units, and error bars represent +/− 1 standard error from mean.