Figure 2.
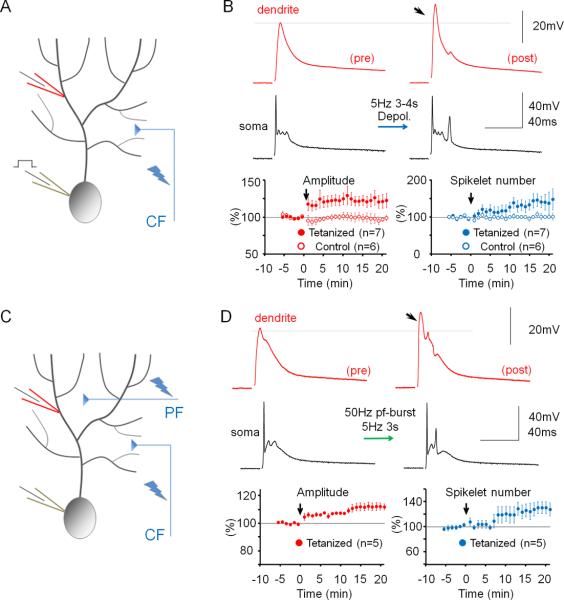
Dendritic patch-clamp recordings reveal activity-dependent changes in dendritic responsiveness. (A) Recording configuration for the experiments shown in (B). Responses to CF activation were recorded before and after repeated injection of depolarizing currents into the soma. (B) The somatic depolarization protocol enhances CF responses (arrow). Lower left: Time graph showing changes in the amplitude of dendritically recorded CF responses after tetanization (closed dots; n=7) and under control conditions (open dots; n=6). Lower right: Time graph showing associated changes in the number of spikelets in the complex spike after tetanization (closed dots; n=7) and under control conditions (open dots; n=6). (C) Recording configuration for the experiments shown in (D). Responses to CF activation were recorded before and after 50Hz PF tetanization. (D) 50Hz PF burst stimulation causes an increase in dendritic CF response amplitudes (lower left) and the spikelet number (lower right; n=5). Arrows indicate tetanization. Error bars indicate SEM.