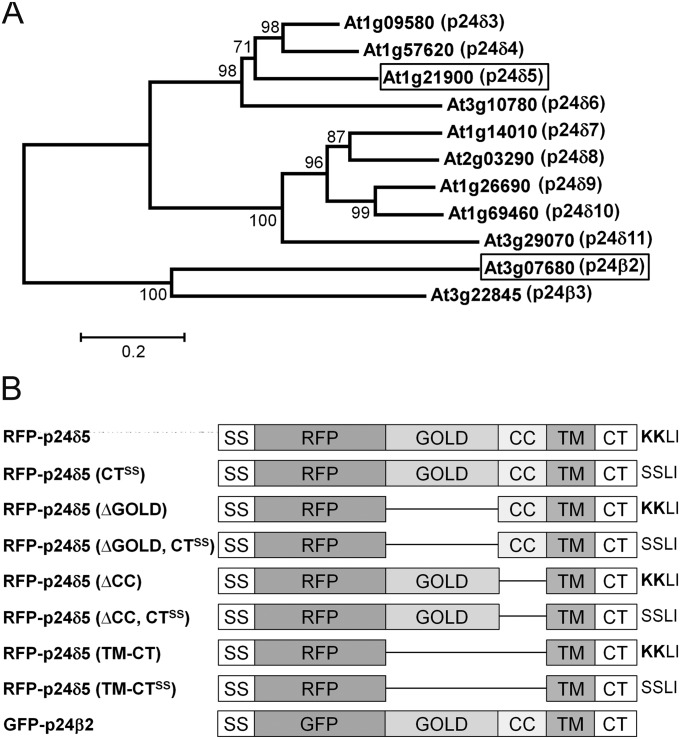
Fig. 1.
The p24 family in Arabidopsis. (A) A phylogenetic tree containing the δ and β subfamilies of p24 proteins in Arabidopsis. A multiple alignment of the p24 proteins was constructed using ClustalW and the tree was generated from this alignment using the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software (MEGA, version 5.03) with the Neighbor–Joining method. The numbers beside the branches represent bootstrap percentage based on 1000 replications. The names assigned to these proteins, following the nomenclature proposed by Dominguez et al. (1998), are shown next to the AGI code. The two proteins analysed in this study, p24δ5 and p24β2, are highlighted. (B) Schematic representation of the RFP–p24δ5 and GFP–p24β2 constructs used in this study, including the different domains of p24δ5 and p24β2. SS, signal sequence; RFP/GFP, red or green fluorescent proteins; GOLD, domain involved in Golgi dynamics (see text for details); CC, coiled-coil domain; TM, transmembrane domain; CT, cytoplasmic tail, which in p24δ5 contains a dilysine (KKXX) motif; CTSS, cytoplasmic tail with the two lysines replaced by serines; ΔGOLD or ΔCC, deletion mutants lacking the GOLD or the CC domains; TM-CT, deletion mutant containing only the transmembrane domain and the cytosolic tail.