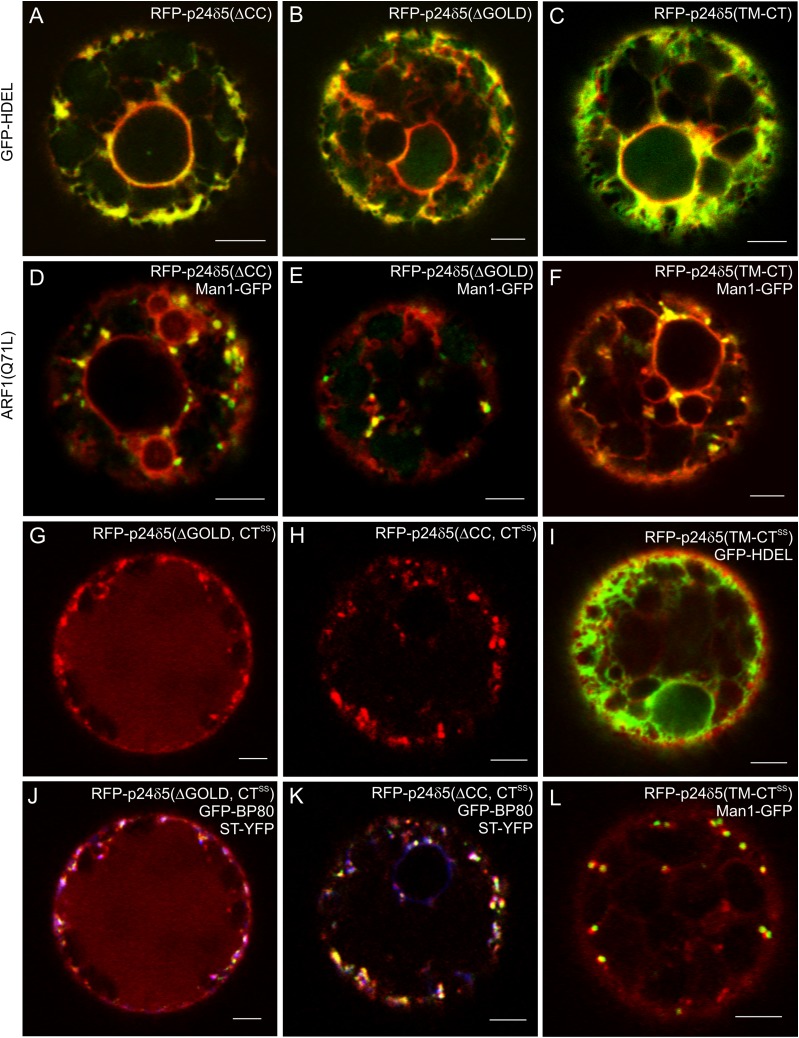
Fig. 5.
RFP–p24δ5 deletion mutants localize to the ER but cycle between the ER and the Golgi, whilst mutants lacking the dilysine motif are transported to the pre-vacuolar compartment and the vacuole. (A–L) Transient gene expression in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. (A–C) RFP–p24δ5 deletion mutants lacking the coiled-coil domain (ΔCC) (A), the GOLD domain (ΔGOLD) (B), or both (TM-CT) (C) show a typical ER pattern and co-localize with the ER marker GFP–HDEL. (D–F) RFP–p24δ5 deletion mutants lacking the coiled-coil domain (ΔCC) (D), the GOLD domain (ΔGOLD) (E), or both (TM-CT) (F) co-localize partially with Man1–GFP in Golgi-like punctae upon ARF1(Q71L) mutant expression. (G and J) An RFP–p24δ5 dilysine mutant lacking the GOLD domain (ΔGOLD, CTSS) shows a prominent vacuolar labelling but it also co-localizes partially in punctae with Golgi (ST–YFP; blue) or PVC (GFP–BP80; green) markers. (H and K) An RFP–p24δ5 dilysine mutant lacking the coiled-coil domain (ΔCC, CTSS) shows a weak vacuolar labelling but it also co-localizes partially in punctae with Golgi (ST–YFP; blue) or PVC (GFP–BP80; green) markers. (I and L) An RFP–p24δ5 dilysine mutant with the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmic tail (TM-CTSS) co-localizes partially with the ER marker GFP–HDEL and the Golgi marker Man1–GFP. Scale bars=5 μm.