Figure 1.
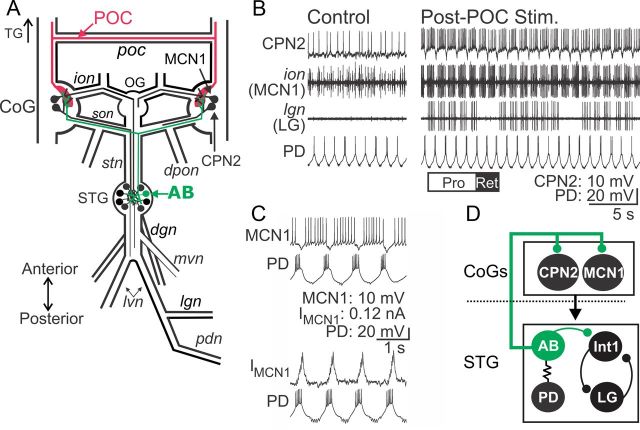
POC neurons activate MCN1 and CPN2 to trigger a particular version of the gastric mill rhythm. A, Schematic of the STNS illustrating the axon pathways of projection (MCN1, CPN2), CPG feedback (AB), and extrinsic input (POC) neurons. There is a single MCN1 and CPN2 in each CoG, ∼100 POC axons entering each CoG, and a single AB neuron in the STG. For clarity, the complete axonal pathways of MCN1 and CPN2 are only illustrated unilaterally. Abbreviations: Ganglia: CoG, Commissural ganglion; OG, oesophageal ganglion; STG, stomatogastric ganglion. Nerves: dgn, dorsal gastric nerve; dpon, dorsal posterior oesophageal nerve; ion, inferior oesophageal nerve; lgn, lateral gastric nerve; lvn, lateral ventricular nerve; mvn, medial ventricular nerve; pdn, pyloric dilator nerve; poc, post-oesophageal commissure; son, superior oesophageal nerve; stn, stomatogastric nerve. Neurons: AB, anterior burster; CPN2, commissural projection neuron 2; MCN1, modulatory commissural neuron 1; POC, post-oesophageal commissure. B, Left, During control conditions, MCN1 and CPN2 are weakly active, there is an ongoing pyloric rhythm (PD neuron) and there is no gastric mill rhythm (LG neuron silent in the lgn recording). Right, POC stimulation triggers a gastric mill rhythm that is characterized by rhythmic interruptions in the activity of MCN1, CPN2, and the gastric mill protractor motor neuron LG that are time-locked to the ongoing pyloric rhythm (e.g., PD neuron) (Blitz et al., 2008). The white (“PRO”) and black (“RET”) bars indicate protraction and retraction phases of one cycle of the gastric mill rhythm. C, Pyloric (PD neuron)-timed inhibition is evident in a MCN1 recording as barrages of IPSPs that transiently eliminate MCN1 activity (top) and IPSCs in voltage-clamp recording mode (bottom). MCN1 recordings in both panels are from the same preparation. D, Schematic highlighting the feedback inhibitory synapse from AB onto MCN1 and CPN2 in the CoGs (Blitz and Nusbaum, 2008). The AB soma is in the STG, from which it projects an axon to innervate each CoG and cause glutamatergic inhibition of projection neurons, including MCN1 and CPN2 (Blitz and Nusbaum, 1999). The dotted line indicates spatial separation of the CoGs from the STG. AB is electrically coupled to both PD neurons, causing them to fire during the same phase of the pyloric rhythm (Marder and Eisen, 1984a). Thus, activity of the more readily accessible PD neuron is often used as a marker of AB activity.