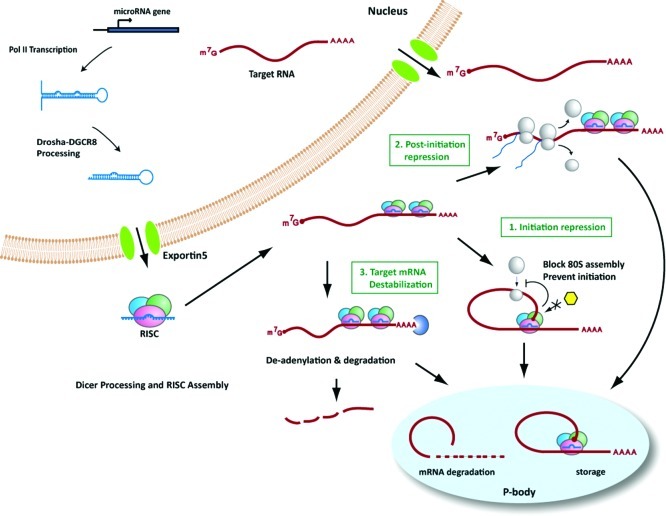
Figure 5.
microRNA function. After loading with Ago proteins to form functional RISCs, miRNA-guided RISCs bind to the target mRNAs and inhibit target gene expression. Currently, there are at least three mechanisms that have been linked to miRNA-mediated gene silencing. (1) Repression of translation initiation. In this case, miRISCs inhibit initiation of translation by affecting the eIF4F-cap recognition, 40S small ribosomal subunit recruitment, and/or by inhibiting incorporation of the 60S subunit and formation of the 80S ribosomal complex. Some of the target mRNAs bound by miRISC is transported into P-bodies for storage and may re-enter the translation phase when induced. (2) Postinitiation translational repression. miRISCs could interfere after translation has been initiated by inhibiting elongation of ribosomes, causing ribosome drop-off from mRNAs, and/or by facilitating degradation of newly synthesized nascent peptides. (3) Destabilization of target mRNAs. miRISCs could cause destabilization of target mRNAs by directly interacting with CCR4-containing deadenylation complexes and facilitating the deadenylation of poly A tails of target mRNAs. Following deadenylation, the 5′ end-capping structures of target mRNAs are also removed by the DCP1–DCP2 complex.