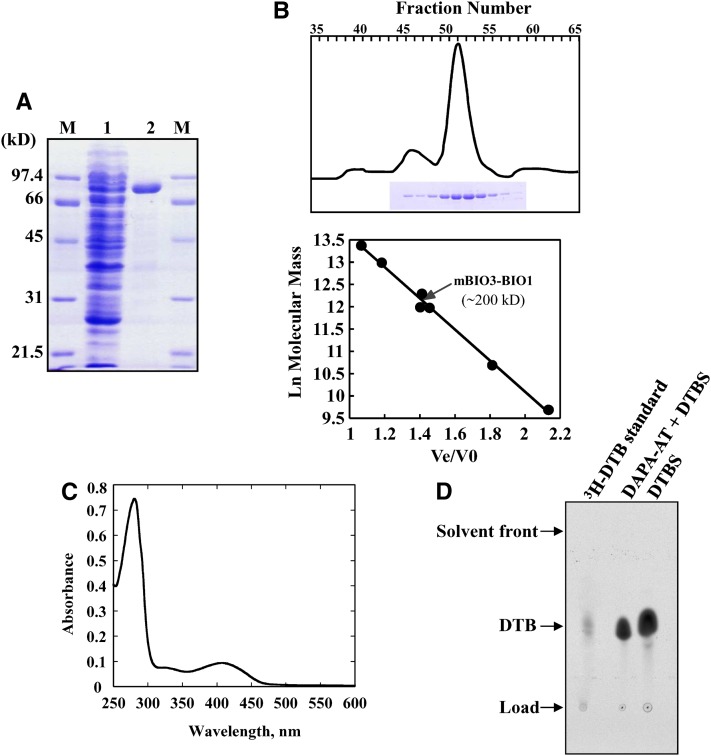
Figure 3.
Physicochemical and Biochemical Properties of Recombinant Arabidopsis mBIO3-BIO1.
(A) Documentation of mBIO3-BIO1 purification on nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid-agarose resin. Polypeptides were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Lane 1, soluble proteins (25 µg) from E. coli Rosetta cells producing mBIO3-BIO1; lane 2, proteins eluted from the column (10 µg); lanes M, molecular mass markers.
(B) Purification and molecular mass estimation of native mBIO3-BIO1 by gel filtration. Purified protein was resolved by chromatography onto a Superdex 200 HiLoad column (2.6 × 60 cm; GE Healthcare). Eluted fractions (3 mL) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (top panel). Standards proteins for column calibration (bottom panel) were as follows: thyroglobulin (669 kD), ferritin (443 kD), catalase (232 kD), γ-globulin (158 kD), aldolase (158 kD), ovalbumin (43 kD), and myoglobulin (17 kD). Ve, elution volume; V0, void volume.
(C) Spectroscopy analysis of purified recombinant mBIO3-BIO1. Absorption spectrum was recorded at 30°C in 100 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 7.5, in the presence of 20 µM pure enzyme.
(D) HP TLC detection of DTB produced by recombinant mBIO3-BIO1. The overall (DAPA-AT + DTBS) reaction and DTBS reaction were performed by measuring the formation of acid-stable [14C]-DTB from acid-labile H14CO3 as described in Methods. Assays contained 0.2 nmol (DAPA-AT + DTBS reaction) or 0.1 nmol (DTBS reaction) enzyme, and reaction mixtures were incubated for 120 or 20 min, respectively. [14C]-DTB produced was separated by TLC and detected by phosphor imaging analysis (Picciocchi et al., 2001). Migration was compared with that of authentic [3H]-DTB standard (Rf = 0.53).
[See online article for color version of this figure.]